20 June 2020: Clinical Research
Detection of Dysplastic Liver Nodules in Patients with Cirrhosis Using the Multi-Arterial CAIPIRINHA-Dixon-TWIST-Volume-Interpolated Breath-Hold Examination (MA-CDT-VIBE) Technique in Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Ling Fei Guo 1ABCDE , Guihua Gao 2BDF , Zhenguo Yuan 1ADG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.922618
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e922618
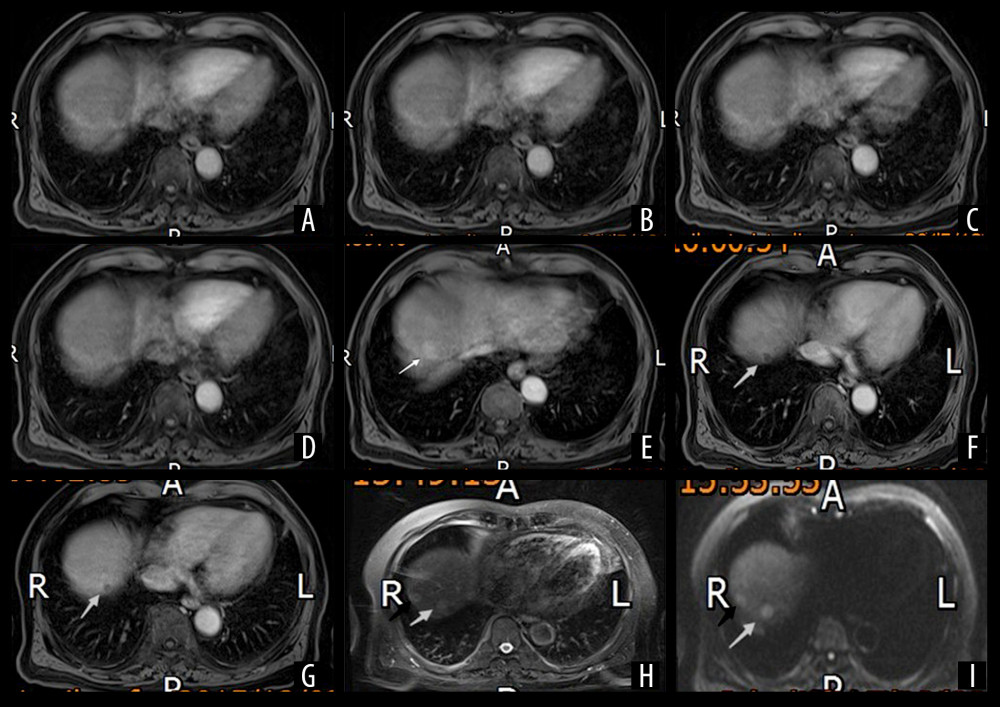
Figure 1 Multi-Arterial CAIPIRINHA-Dixon-TWIST–Volume-Interpolated Breath-Hold Examination (MA-CDT-VIBE) of a 73-year-old male patient with a history of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection for more than ten years and ultrasound diagnosis of liver cirrhosis Two round nodules are shown in the right posterior lobe (VII) (black and white arrows). Panel A–E show the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth arterial subphases of the MA-CDT-VIBE sequence, respectively. Panel D (fourth arterial subphase) is an equivalent standard arterial phase (ESAP) image. Panel F is a portal vein phase image. Panel G is a delayed phase image. Panel H is an image obtained by T2-weighted imaging (T2WI). Panel I is an image obtained by diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) (b = 800). The images show that the two enhanced nodules were not clearly shown in the first through fourth subphases. However, significantly enhanced lesions were observed in the fifth arterial phase. White arrows indicate nodules with decreased signals in the portal vein phase (Panel F) and delayed phase (Panel G) exhibiting a ‘fast in and fast out’ type. The black arrows indicate nodules with a nonsignificant decrease in the signals in the portal vein phase and delayed phase. The two enhanced lesions show high signals on T2WI. The diffusion of the signals was limited on DWI (b=800), which shows high signals.


