02 October 2020: Lab/In Vitro Research
Circular RNA circ_C16orf62 Suppresses Cell Growth in Gastric Cancer by miR-421/Tubulin beta-2A Chain (TUBB2A) Axis
Yanfeng Jin 1ABCDE , Shanshan Zhang 1BCDEF , Li Liu 2BCDE*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.924343
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e924343
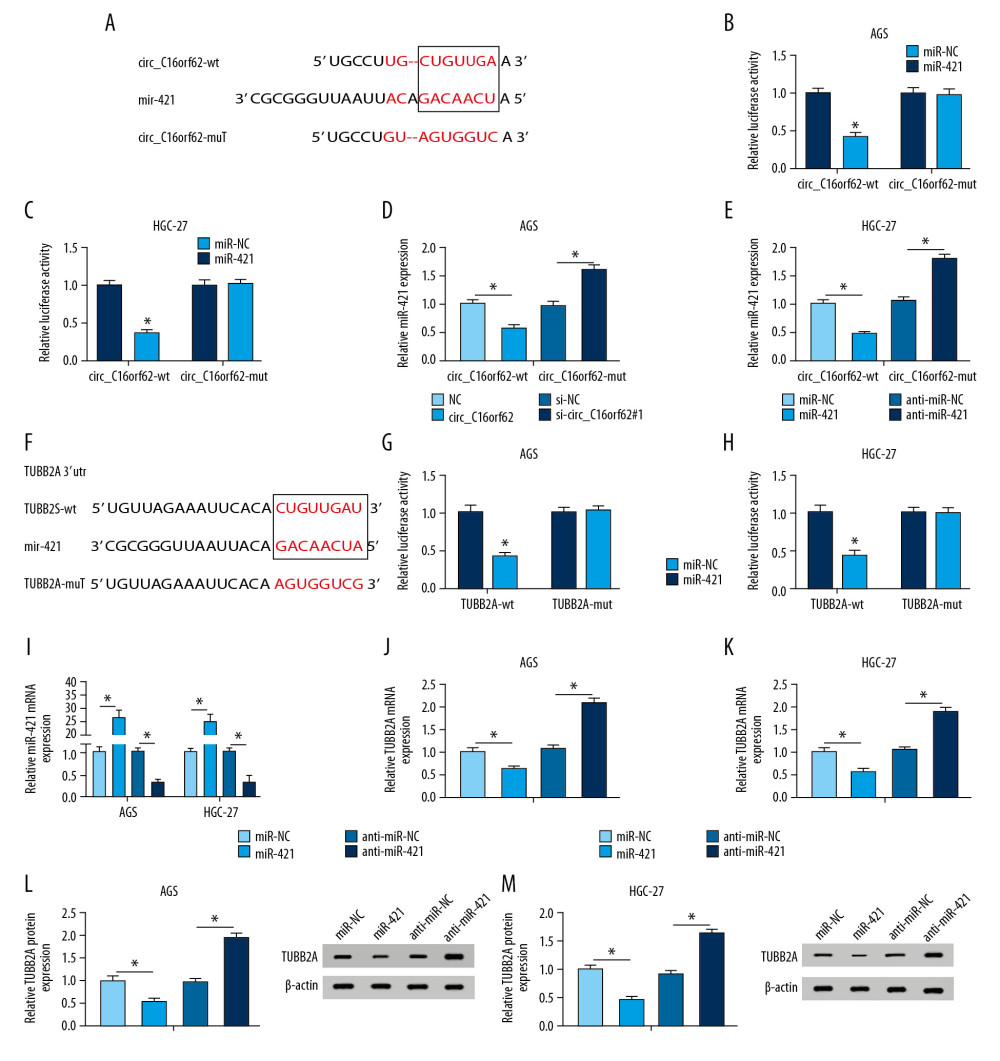
Figure 6 Circ_C16orf62 and TUBB2A bound to miR-421in GC cells. (A) The binding sites between circ_C16orf62 and miR-421 were predicted by bioinformatics software StarBase3.0. (B, C) The binding relationship between circ_C16orf62 and miR-421were testified by dual-luciferase reporter assay. (D, E) MiR-421 level was measured in AGS and HGC-27 transfected with NC, circ_C16orf62, si-NC and si-circ_C16orf62#1. (F) The binding sequences between TUBB2A and miR-421 were predicted by bioinformatics software Targetscan. (G, H) Relative luciferase activity was determined by dual-luciferase reporter assays in AGS and HGC-27cells co-transfected with reporter plasmid (TUBB2A-wt/TUBB2A-mut) and miR-421 or miR-NC. (I) Transfection efficiency of miR-421 mimic or anti-miR-421 was detected by RT-qPCR assay. (J, K) The effects of miR-421 overexpression or miR-421 knockdown on TUBB2A mRNA level were tested by RT-qPCR assay. (L, M) TUBB2A protein level was examined in miR-421 or anti- miR-421-transfected AGS and HGC-27 cells. * P<0.05.


