13 November 2020: Database Analysis
Association of Thiamine Intake with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection in American Women: A Secondary Data Analysis Based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2003 to 2016
Yue-xi Zhou 1BCE , Fang-fang Zhu 1BE , Chi Chen 2C , Ying-xuan Zhang 1D , Xiao-li Lv 1F , Jing-wei Li 1F , Song-ping Luo 3AG** , Jie Gao 3AG**DOI: 10.12659/MSM.924932
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e924932
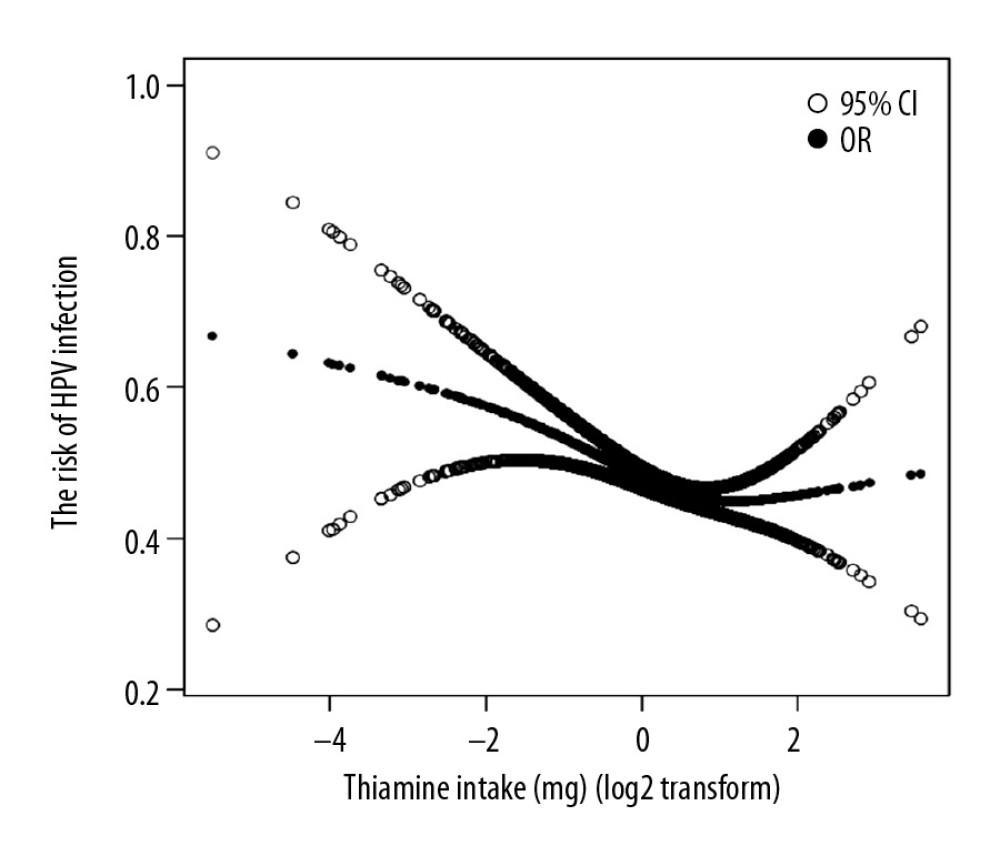
Figure 2 Correlation between the risk of HPV infection and thiamine intake. The inflection point of thiamine intake was 2.07 mg. On the left side of the inflection point (thiamine intake ≤2.07 mg), the difference in thiamine intake of log2 transform is related to the 0.82 difference in HPV infection. On the right side of the inflection point, we did not observe a correlation between HPV infection and thiamine intake (β=1.40, 95% CI: 0.93, 2.10).


