26 July 2020: Lab/In Vitro Research
Vitamin D Attenuates Hypoxia-Induced Injury in Rat Primary Neuron Cells through Downregulation of the Dual Oxidase 1 (DUOX1) Gene
Panpan Cui 12BD , Yan Wang 1AC , Yanzhong Li 1AE* , Lei Ge 3FDOI: 10.12659/MSM.925350
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e925350
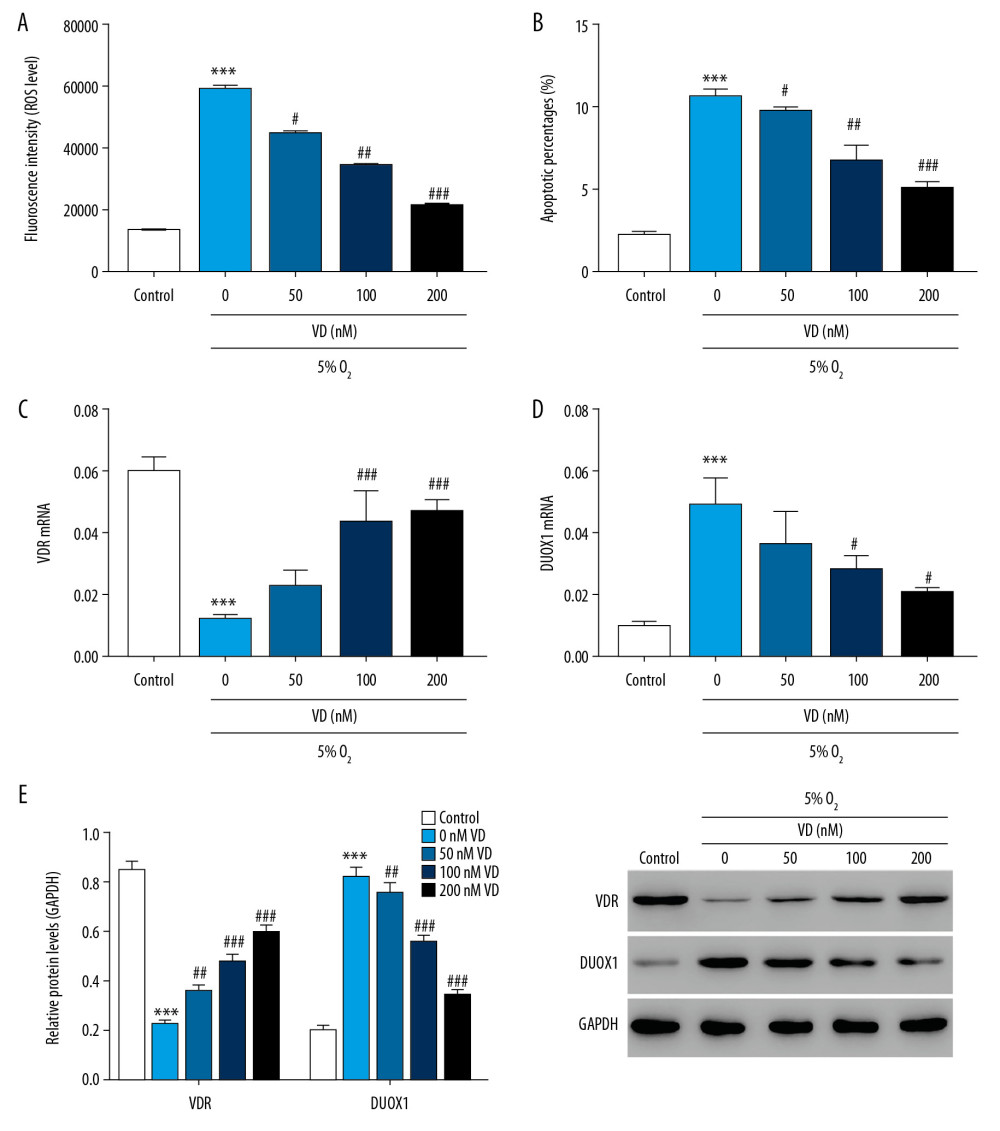
Figure 2 Vitamin D attenuated hypoxia-induced injury in rat primary neuron cells. (A) ROS level was detected by flow cytometry after treatment with different concentrations of vitamin D. (B) Apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry after treatment with different concentrations of vitamin D. (C, D) The mRNA expression of VDR and DUOX1 was detected by Q-PCR after treatment with different concentrations of vitamin D. (E) The protein expression of VDR and DUOX1 was detected by western blot after treatment with different concentrations of vitamin D. *** P<0.001 versus control; # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 versus 0 nM vitamin D. Control: rat neuron cells cultured under normoxic conditions. ROS – reactive oxygen species; VDR – vitamin D receptor; DUOX1 – dual oxidase 1; Q-PCR – quantitative polymerase chain reaction;


