30 October 2020: Lab/In Vitro Research
Tripartite Motif Containing 52 Positively Regulates NF-κB Signaling by Promoting IκBα Ubiquitination in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Microglial Cell Activation
Pei Zhang AG* , Yimin Wu BE , Ruifeng Li CD , Huicheng Lv D , Baolong Yu FDOI: 10.12659/MSM.925356
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e925356
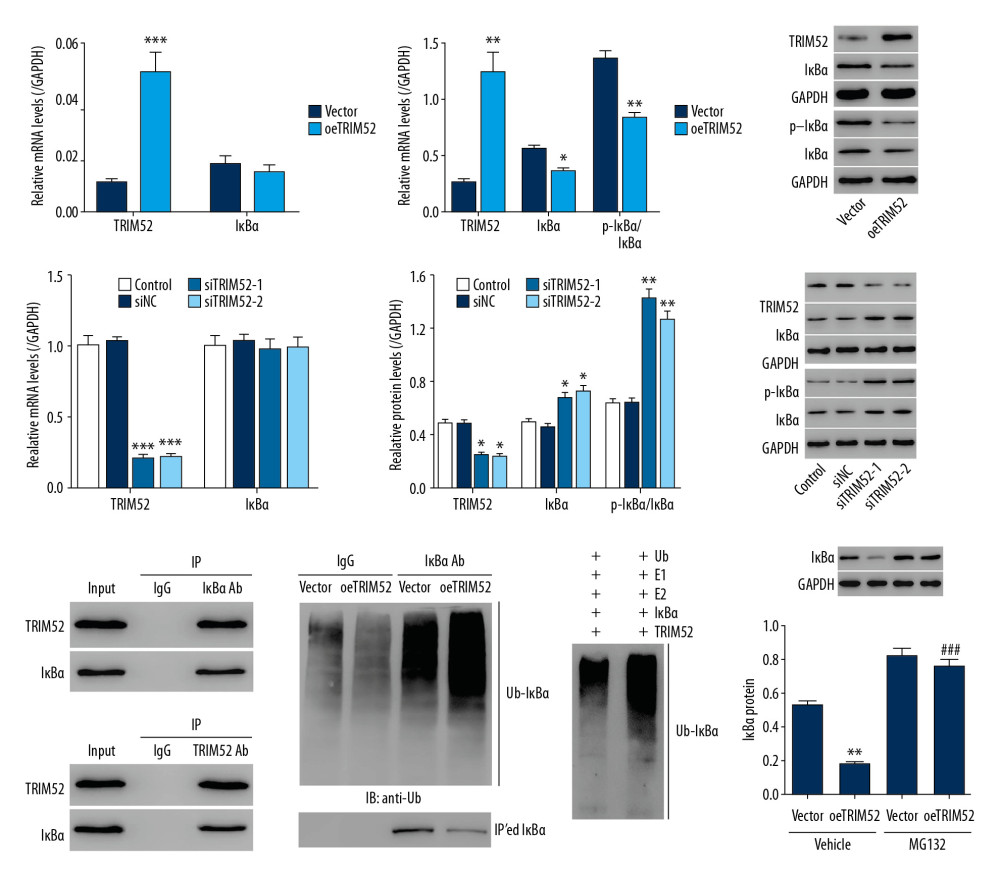
Figure 3 Tripartite motif containing 52 (TRIM52) activated the NF-κB signaling pathway through promotion of IκBα protein ubiquitination. TRIM52 gene overexpression lentivirus transfected rat primary microglial cells: (A) The mRNA expression of TRIM52 and IκBα was detected by Q-PCR. (B) The protein levels of TRIM52, IκBα, and p-IκBα were detected by western blot. TRIM52 gene interference lentivirus transfected rat primary microglial cells: (C) The mRNA expression of TRIM52 and IκBα was detected by Q-PCR. (D) The protein levels of TRIM52, IκBα, and p-IκBα were detected by western blot. (E) Co-IP detected TRIM52 and IκBα interaction in rat primary microglia. (F) Overexpression of TRIM52 gene in rat primary microglia. Western blot was used to detect IκBα ubiquitination. (G) Co-IP detected TRIM52 and IκBα interaction by E3 ligase activity. (H) TRIM52 gene overexpression in rat primary microglial cells was treated with 10 μmol/L MG132 (proteasome inhibitor). Western blot was used to detect IκBα protein expression. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs. Vector, siNC or Vehicle+Vector; ### P<0.001 vs. Vehicle+oeTRIM52.


