08 September 2020: Lab/In Vitro Research
Overexpression of Linc 4930556M19Rik Suppresses High Glucose-Triggered Podocyte Apoptosis, Fibrosis and Inflammation via the miR-27a-3p/Metalloproteinase 3 () Axis in Diabetic Nephropathy
Hong Fan 1ABCE , Weiwei Zhang 2BC*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.925361
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e925361
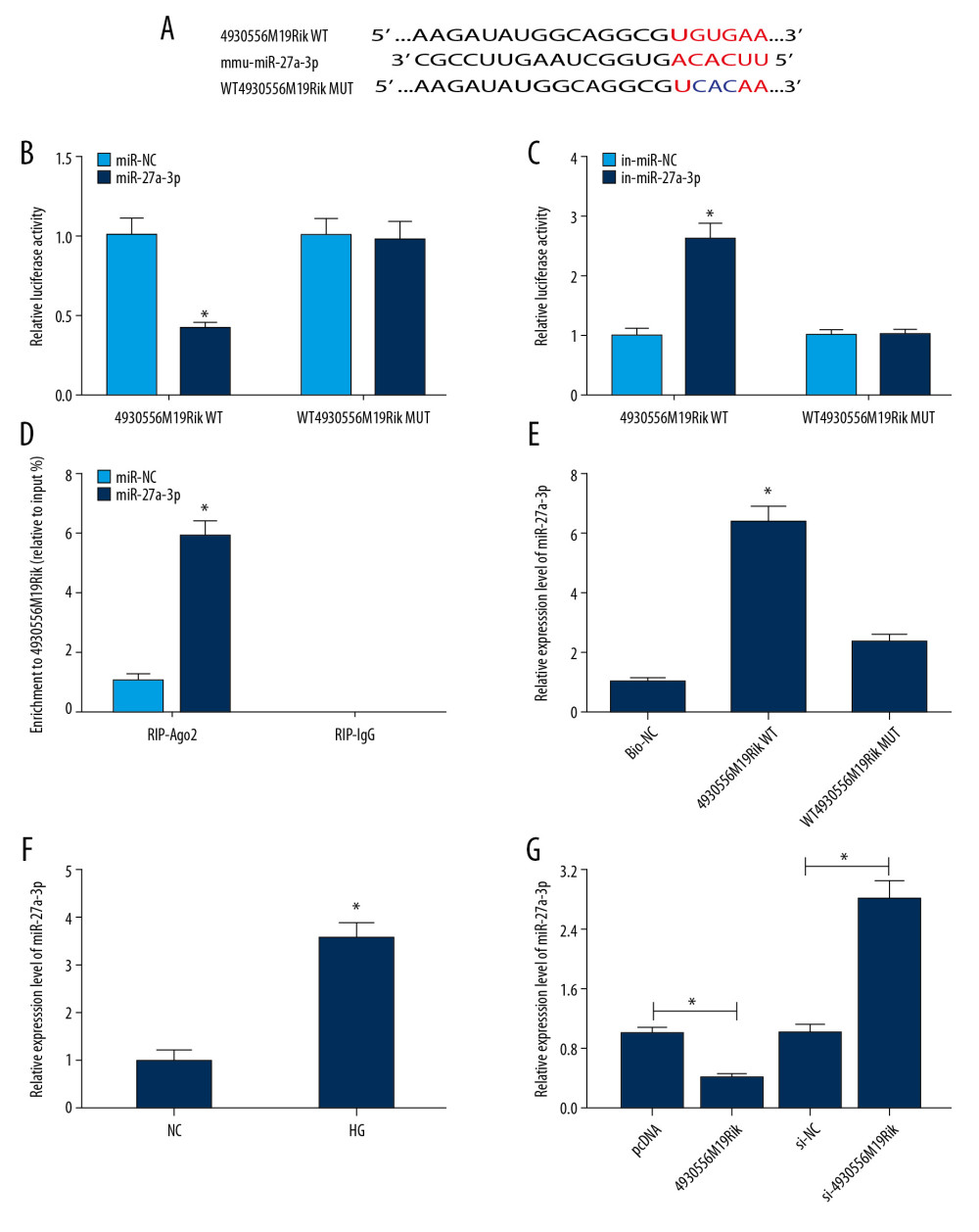
Figure 3 MiR-27a-3p was a direct target of 4930556M19Rik. (A) Complementary sequences between 4930556M19Rik and miR-27a-3p were predicted by diana_tools-lncbasev2. (B, C) Luciferase activity in podocytes co-transfected with miR-27a-3p, miR-NC, in-miR-27a-3p or in-miR-NC and 4930556M19Rik WT or 4930556M19Rik MUT was measured by dual-luciferase reporter assay. (D) After podocytes were transfected with miR-27a-3p or miR-NC, enrichment of 4930556M19Rik in Ago2 or IgG immunoprecipitation complexes was analyzed by RIP assay and qRT-PCR assay. (E) Relative expression of miR-27a-3p in podocyte lysates was determined by qRT-PCR assay following RNA pull-down assay. (F) MiR-27a-3p level in HG-induced podocytes and corresponding controls was detected using qRT-PCR assay. (G) Podocytes were transfected with pcDNA, 4930556M19Rik, si-NC or si-4930556M19Rik and then treated with HG. Next, the expression level of miR-27a-3p in podocytes was measured using qRT-PCR assay. * P<0.05.


