21 September 2020: Lab/In Vitro Research
P2X7 Receptor (P2X7R) of Microglia Mediates Neuroinflammation by Regulating (NOD)-Like Receptor Protein 3 (NLRP3) Inflammasome-Dependent Inflammation After Spinal Cord Injury
Xiao Fan 12ABCEF* , Wei Ma 3ABCEF* , Yingyu Zhang 1BCD , Li Zhang 24AFG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.925491
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e925491
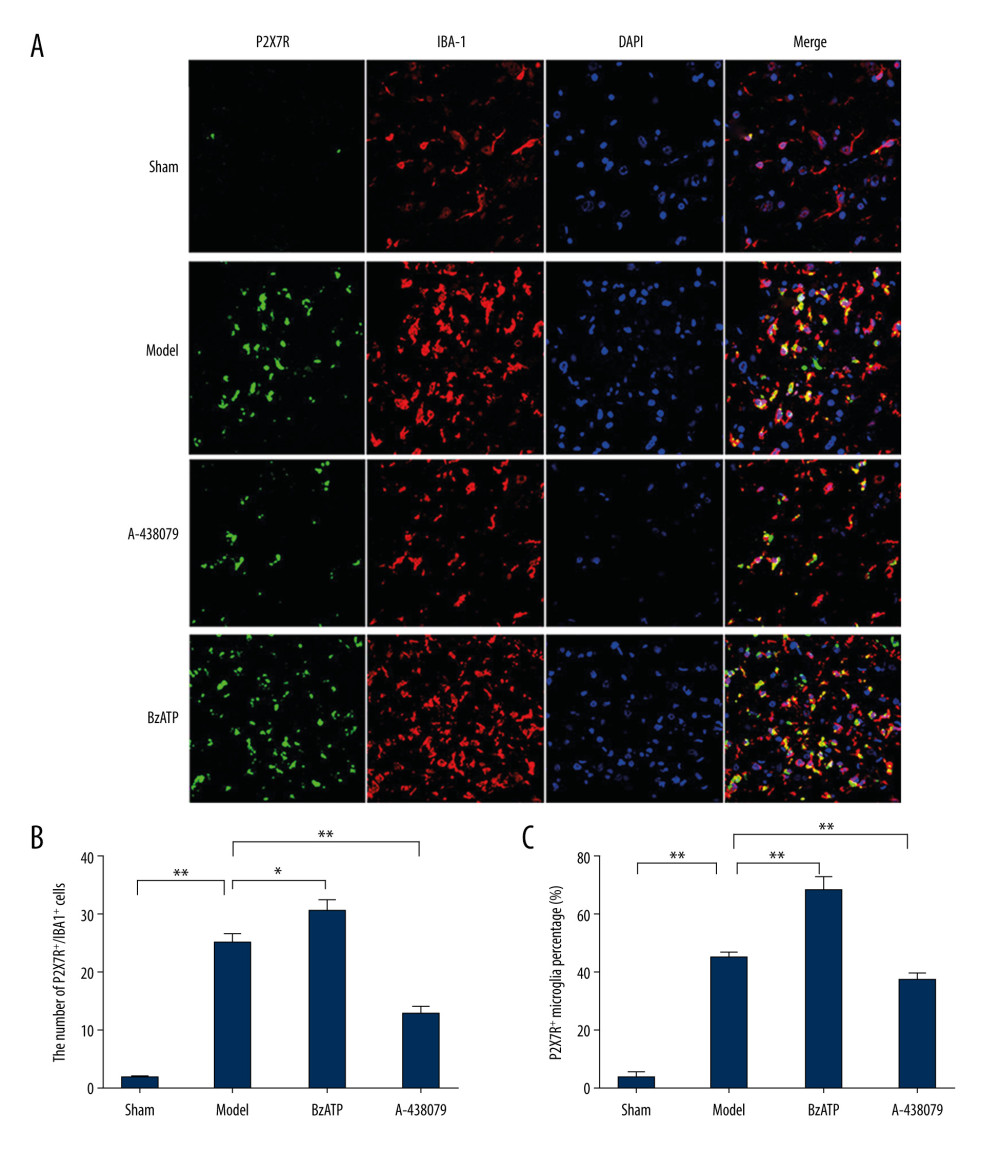
Figure 1 Immunofluorescence detected P2X7R of microglia in spinal cord. (A) P2X7R (P2X7R+, green) and IBA-1 (IBA-1+, red) co-expressed as P2X7R of microglia (P2X7R+/IBA-1+, yellow) that were overexpressed after spinal cord injury and BzATP intervention, and, compared to the morphology of microglia in the sham group, the morphology of activated microglia after injury changed to large soma and short irregular processes, revealing that many microglia in spinal cord became active after spinal cord injury. (B) The number of P2X7R of microglia (P2X7R+/IBA-1+) increased notably after spinal cord injury compared to the sham group (** P<0.01), and, compared to the model group, BzATP increased the number of P2X7R of microglia (* P<0.05) while A-438079 significantly decreased the number of P2X7R of microglia (** P<0.01). (C) The P2X7R-positive microglia percentage was clearly increased after spinal cord injury compared to the sham group (** P<0.01), and, compared to the model group, BzATP accounted for a significantly increased P2X7R-positive microglia proportion (** P<0.01) while A-438079 accounted for a significantly reduced P2X7R-positive microglia proportion (** P<0.01).


