18 November 2020: Animal Study
Altered Inflammatory Pathway but Unaffected Liver Fibrosis in Mouse Models of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Involving Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 1 Knockout
Ying Lei BCDE* , Tianxiao Yang BEFG* , Aijing Shan CDG , Wei Di BC , Mengyao Dai EFG , Jingminjie Nan B , Dongxue Liu B , Yanan Cao AEG , Xiuli Jiang AEG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.926187
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e926187
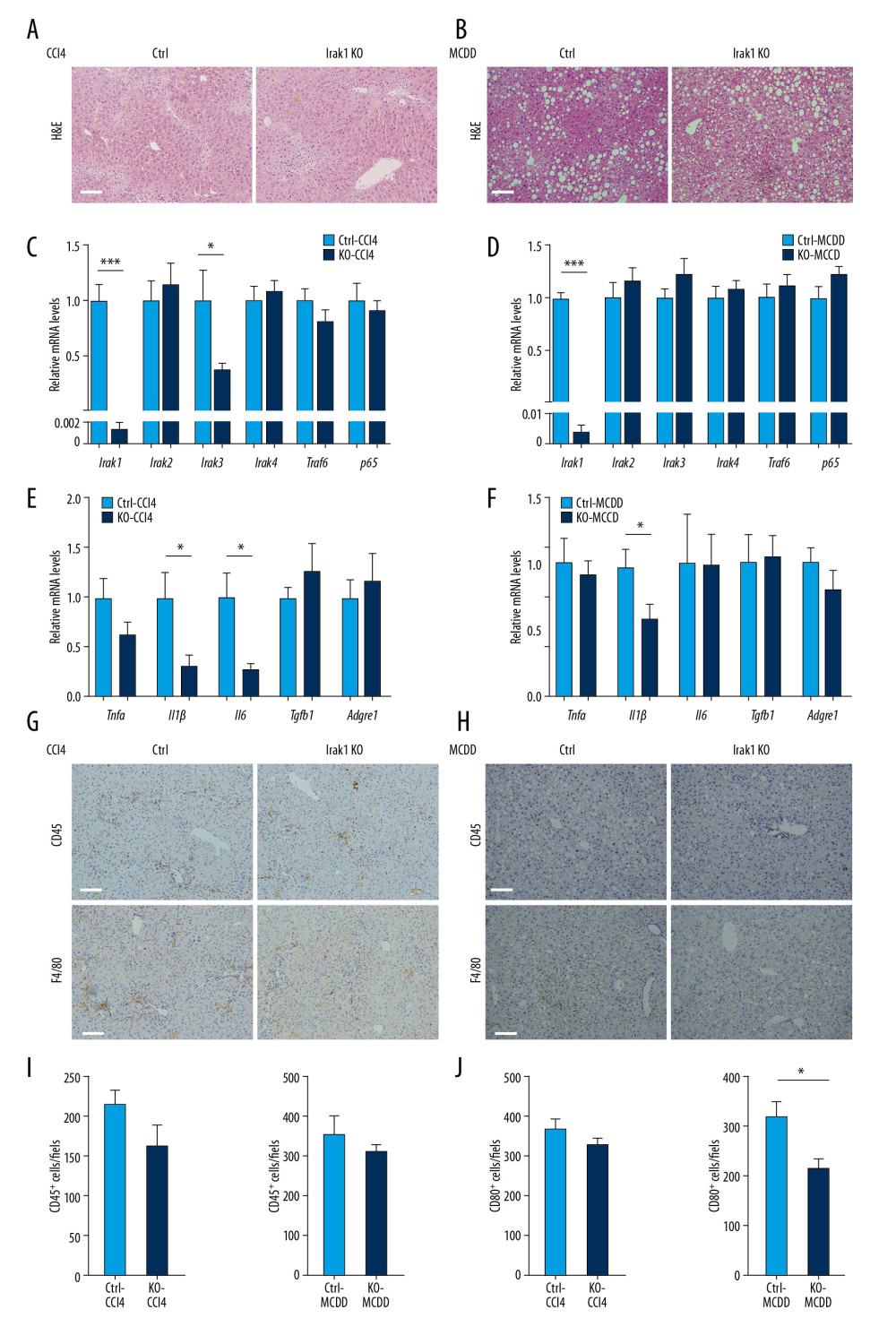
Figure 3 Effects of Irak1 KO on key pro-inflammatory factors and inflammatory cell infiltration in the livers in mouse models of NASH. (A, B) Representative H&E-stained liver sections of Irak1 KO and control mice following (A) treatment with CCl4 for 8 weeks or (B) MCDD feeding for 6 weeks. Scale bars, 100 μm. (C, D) Hepatic Irak1, Irak2, Irak3, Irak4, Traf6, and p65 mRNA levels in Irak1 KO and control mice following (C) treatment with CCl4 for 8 weeks (n=5) or (D) MCDD feeding for 6 weeks (n=5–6). (E, F) Hepatic Tnfα, Il1β, Il6, Tgfb1, and Adgre1 mRNA levels in Irak1 KO and control mice following (E) treatment with CCl4 for 8 weeks (n=5) or (F) MCDD feeding for 6 weeks (n=5–6). (G, H) Representative CD45 (upper part) and F4/80 (bottom part) positively-stained liver sections of Irak1 KO and control mice following (G) treatment with CCl4 for 8 weeks or (H) MCDD feeding for 6 weeks. Scale bars, 100 μm. (I, J) Numbers of (I) CD45-positive and (J) F4/80-positive cells per field from Irak1 KO and control mice following CCl4 treatment for 8 weeks (n=3–4, 5 fields per mouse) or MCDD feeding for 6 weeks (n=3–4, 5 fields per mouse). Data represent mean±SEM. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, by t test.


