10 May 2021: Clinical Research
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Language Following Constraint-Induced Aphasia Therapy Primed with Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation in 13 Patients with Post-Stroke Aphasia
Jane B. Allendorfer 1BCDEF* , Rodolphe Nenert 1BCDE , Sangeeta Nair 1CDE , Jennifer Vannest 2ABDE , Jerzy P. Szaflarski 13ABCDEFGDOI: 10.12659/MSM.930100
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e930100
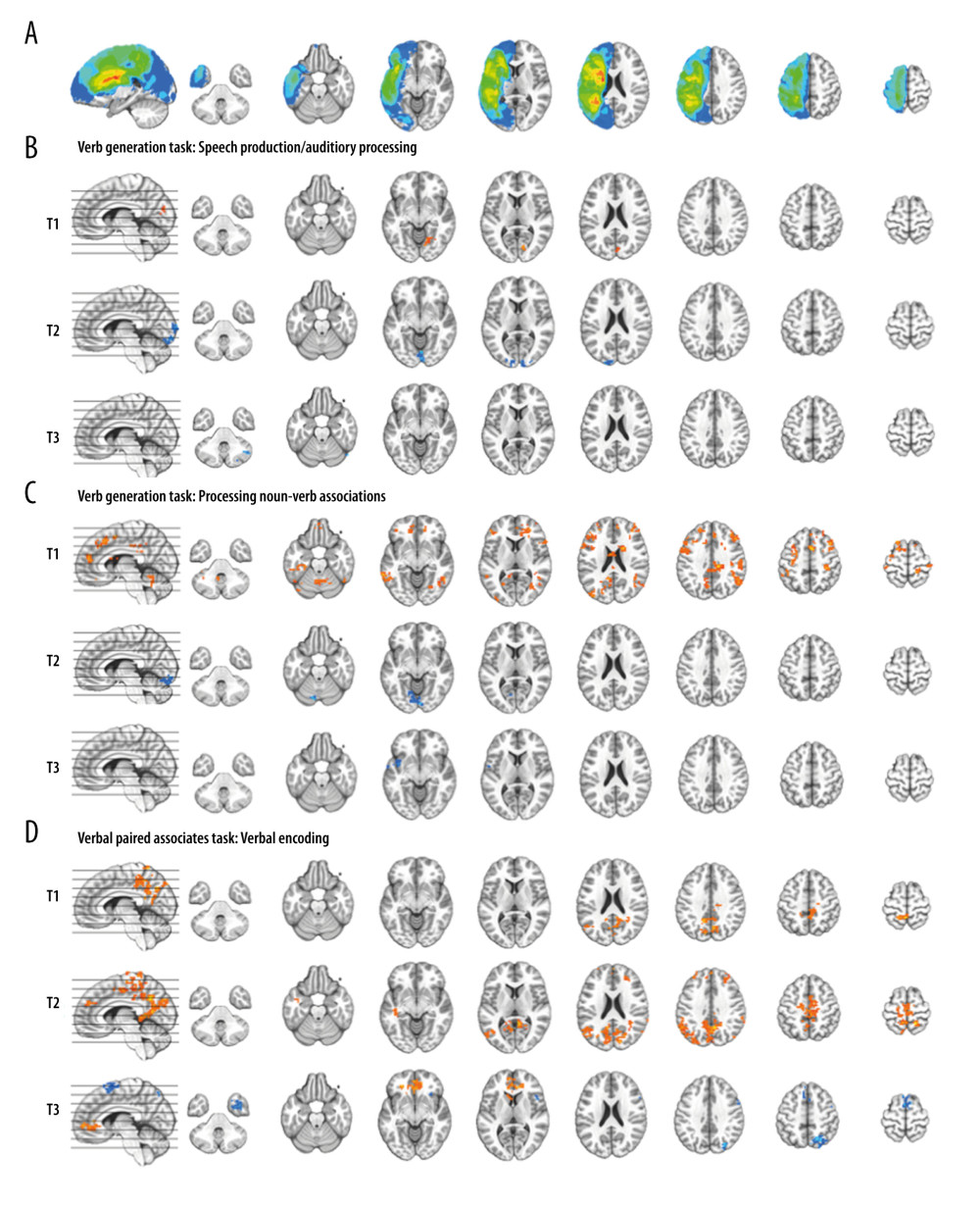
Figure 3 Composite lesion map and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) activation for the 13 participants. The composite lesion map and fMRI task activation maps at baseline (T1), immediately after treatment (T2) and at 3-month follow-up (T3; n=12) are overlaid onto a standard anatomical brain image in Montreal Neurologic Institute space. For all axial slices, left in the image is left in the brain. (A) The composite lesion map color scale ranges from the minimum (n=1 in blue) to the maximum (n=10 in red) number of participants that show overlap of lesions. (B) Statistical maps illustrating whole-brain fMRI activation patterns during speech production/auditory processing (“say verbs” vs “think verbs”) on the verb generation task are diminished at all 3 time points. Activation clusters are significant at corrected p<0.05 (voxelwise p=0.05, cluster threshold of 2079 mm3). (C) Activation related to processing noun-verb semantic associations on the verb generation task (“say verbs” vs “repeat nouns”) are present in frontal, temporal and parietal regions at T1 with minimal activation at T2 and T3. Activation clusters are significant at corrected p<0.05 (voxelwise p=0.05, cluster threshold of 2079 mm3). (D) Statistical maps illustrating whole-brain fMRI activation patterns during verbal encoding (“generate” vs “read”) on the verbal paired associates task are similar at T1 and T2, and differing at T3. Activations are significant at p<0.05, corrected (voxelwise p=0.05, cluster threshold of 1836 mm3).


