03 November 2021: Review Articles
A Review of the Role of Hypoxia in Radioresistance in Cancer Therapy
Wafa Boulefour 1BDEF* , Elise Rowinski 1DF , Safa Louati 234BD , Sandrine Sotton 1E , Anne-Sophie Wozny 234AD , Pablo Moreno-Acosta 5DF , Benoite Mery 1D , Claire Rodriguez-Lafrasse 234D , Nicolas Magne 1234ADDOI: 10.12659/MSM.934116
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e934116
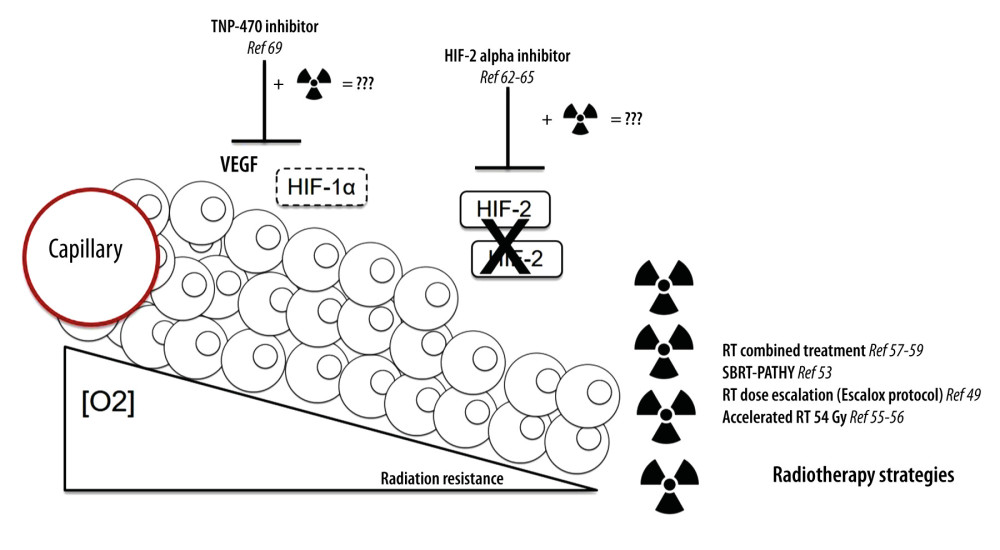
Figure 1 Strategies to overcome hypoxia-induced radioresistanceUnder hypoxic conditions, the HIF-1α subunit translocates to the nucleus and binds HIF-1β. This results in the transcriptional activation of many genes, which plays a role in tumor progression. Both HIF-1 and HIF-2 stimulate transcription of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a crucial regulator of vascular development. Different strategies have already been tested to overcome hypoxia-induced radioresistance. (1) The ESCALOX protocol concluded that dose escalation to large parts of the tumor was associated with the risk of more acute and late toxicity. (2) Stereotaxic body radiation therapy showed very encouraging results for very large unresectable tumors. (3) Accelerated radiotherapy induced tumor radiosensitivity. As perspective, in vitro TNP-470, an angiogenesis inhibitor, could increase tumor oxygenation and radiosensitivity. Likewise, HIF-2α (PT2385) inhibition enhanced radiation sensitivity in a cellular model of lung cancer by promoting apoptotic activity via the p53 pathway. The association of radiotherapy and TNP-470 and/or PT2385 should be investigated.


