30 July 2023: Review Articles
Enhancing Bone Grafting Outcomes: A Comprehensive Review of Antibacterial Artificial Composite Bone Scaffolds
Yi Liu 1AEF* , Liuxing He 1AFG* , Lijia Cheng 1AEFG* , Xinsong Li 1EF , Min Gao 1EF , Qinzhi Li 1E , Jingjing Gao 1EF , Murugan Ramalingam 123FDOI: 10.12659/MSM.939972
Med Sci Monit 2023; 29:e939972
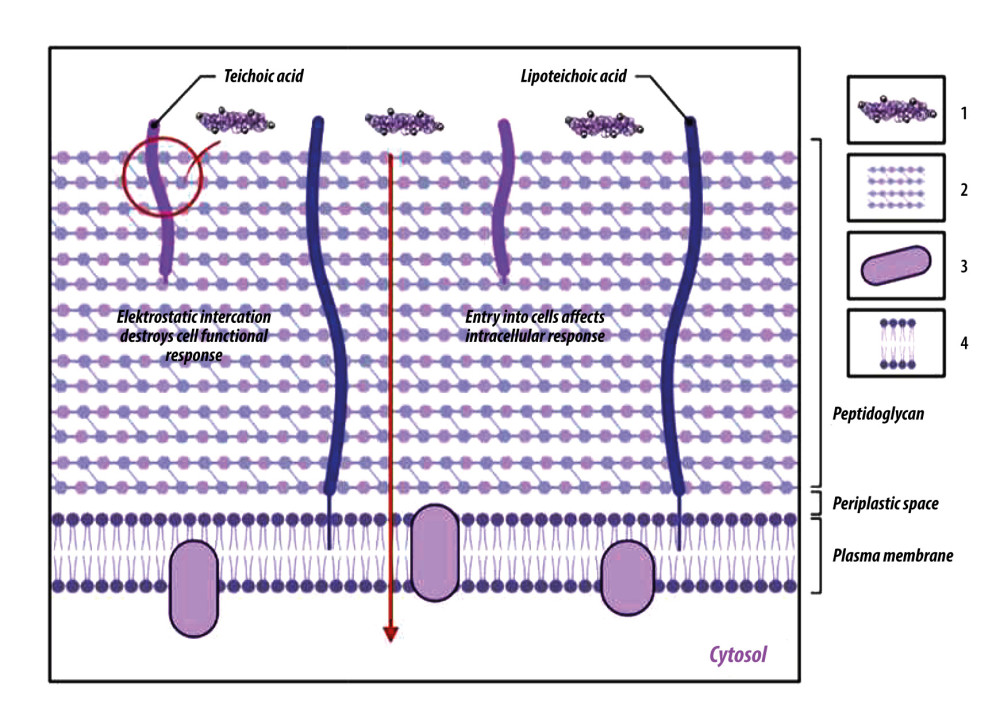
Figure 6 Chitosan antibacterial mechanism model. One is that chitosan particles contain a large amount of positively charged ammonia. These can be electrostatic connected with the negatively charged substances in the outer layer of bacterial cells, adsorbed on the cell surface to form a polymer film, prevent nutrients from entering the cell, and make the negative charge on the cell wall and membrane unbalanced, thus inhibiting cell growth. The other is to penetrate the cell, absorb the anionic substances in the cell, hinder the transcription of genetic material and protein translation, disturb the normal physiological activities of the cell, to achieve the antibacterial effect. 1: Chitosan; 2: Peptidoglycan layer; 3: Membrane protein; 4: Phospholipid. Created with BioRender.com.


