26 January 2024: Lab/In Vitro Research
CTRP13 Mitigates Endothelial Cell Ferroptosis via the AMPK/KLF4 Pathway: Implications for Atherosclerosis Protection
Jie Du 123ABCDEF , Jianjun Wu 12ABC , Youqi Zhang 12CDF , Qi Liu 12CDF , Xing Luo 12ABD , Xingtao Huang 12ABC , Xuedong Wang 12ABC , Fan Yang 12AEF , JingBo Hou 12ABCDEFG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942733
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942733
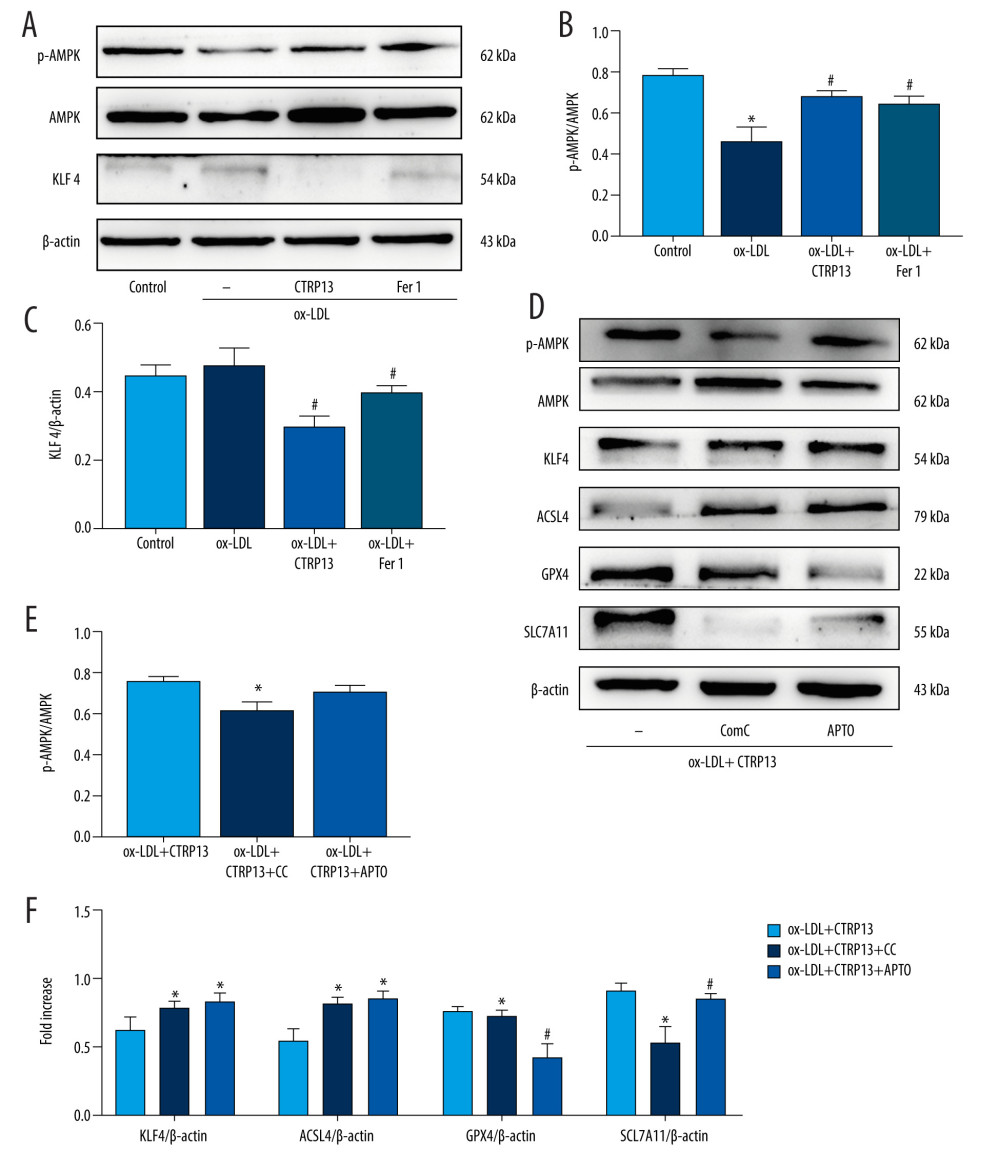
Figure 5 The ferroptosis protective effect of C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein 13 (CTRP13) was attenuated by inhibiting the AMPK/KLF4 pathway. (A) Protein expression levels were measured using Western blotting. The following groups were assessed: (1) Control; (2) oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL); (3) ox-LDL+CTRP13; and (4) ox-LDL+Fer-1. (B, C) Quantitative analysis of phosphorylated AMP-activated kinase (p-AMPK), AMP-activated kinase (AMPK), and Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4). (D–F) The cells were treated with a combination of CTRP13 (450 ng/mL) and ox-LDL (100 μg/mL) for 24 h and subsequently incubated with compound C (5 μmol/L) or inducer of Krüppel-like factor 4 (APTO, 5 μmol/L) for another 24 h. Western blotting results (left panel) and quantitative data (right panel) for ferroptosis-associated protein and p-AMPK, AMPK, and KLF4 are presented. The data are expressed as the mean±SD (n=3–4 per group). Statistical power=0.933291, effect size(r)=0.847233. * P<0.05 vs the control group. # P<0.05 vs the ox-LDL group. The relative protein levels were quantified by Image J software (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA). GraphPad Prism 9.0 software (La Jolla, USA) was used to analyze the data.


