26 January 2024: Lab/In Vitro Research
CTRP13 Mitigates Endothelial Cell Ferroptosis via the AMPK/KLF4 Pathway: Implications for Atherosclerosis Protection
Jie Du 123ABCDEF , Jianjun Wu 12ABC , Youqi Zhang 12CDF , Qi Liu 12CDF , Xing Luo 12ABD , Xingtao Huang 12ABC , Xuedong Wang 12ABC , Fan Yang 12AEF , JingBo Hou 12ABCDEFG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942733
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942733
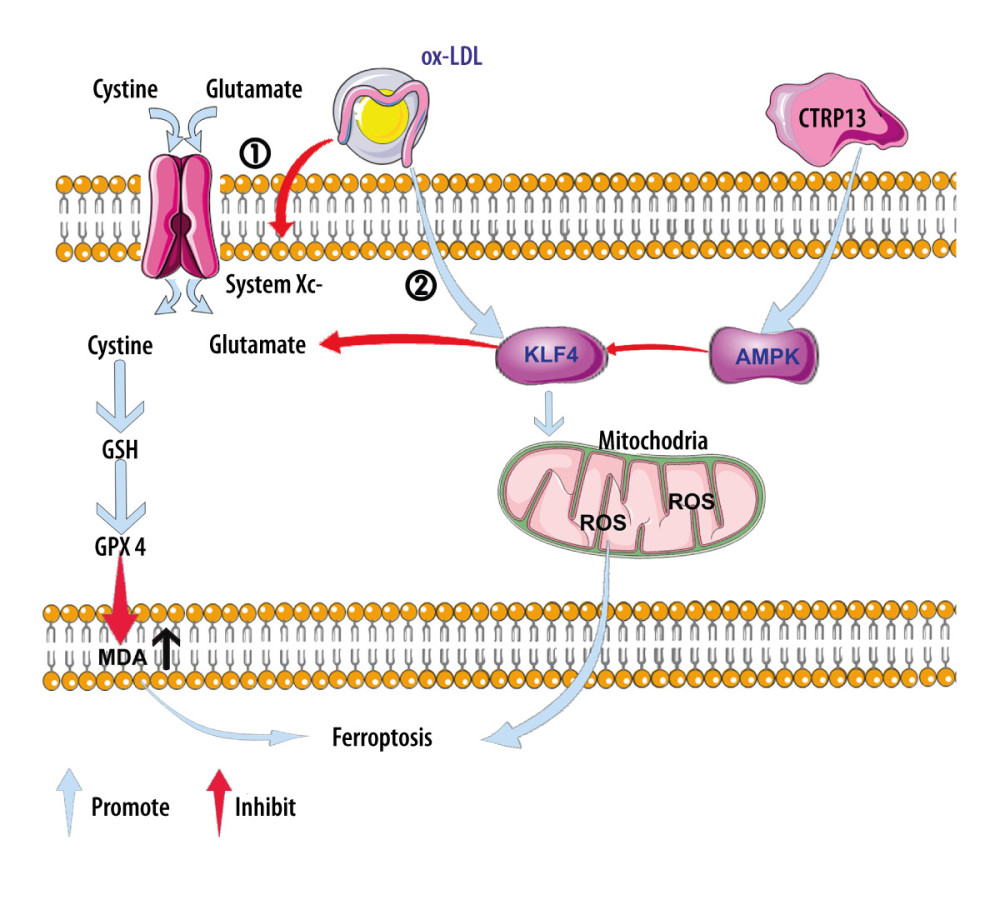
Figure 7 A schematic of the proposed mechanism by which C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein 13 (CTRP13) inhibited oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced ferroptosis. Signal I: ox-LDL depresses the amino acid antiporter solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11/xCT/system xc-), resulting in oxidative damage-induced ferroptosis, while this effect was suppressed by CTRP13 pretreatment. Signal II: ox-LDL activates the Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) pathway and attenuates mitochondrial functioning due to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), while ultimately, CTRP13 treatment inhibits this effect.


