27 June 2022: Clinical Research
Influence of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Voxel Sizes in the Detection of Chemically Induced External Root Resorptions
Mehmet Eray Kolsuz1ABCF, Hakan Eren2BCD, Berkan Çelikten3BCD, Perihan Dalgali EvliDOI: 10.12659/MSM.936160
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e936160
Abstract
BACKGROUND: External root resorption usually does not present a clinical sign or symptom, and, therefore, diagnosis is mainly based on radiographic examination. Many studies confirmed the advantage and accuracy of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) in evaluating root resorptions. We aimed to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of CBCT images of chemically induced external root resorptions on extracted human teeth taken in different voxel sizes.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: In this in vitro study, 36 maxillary and 36 mandibular human incisor teeth, extracted owing to periodontal disease, were used. External resorption cavities were created on the buccal and proximal surfaces by using 10% hydrochloric acid with different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min. Resorption cavities in different depths were induced to simulate different levels of external resorption. CBCT images were taken with Planmeca Promax 3D Max CBCT (Planmeca, Helsinki, Finland) in 4 different voxel sizes: 400, 200, 150, and 100 μm.
RESULTS: There was no statistically significant difference between interobserver and intraobserver reliability. Higher observer agreement was obtained for 100-μm and 150-μm voxel sizes. For detection of external root resorption defects, interobserver agreement was highest for the 100-μm voxel size and when defects were located on the proximal side of the samples. The highest k values were obtained for samples kept in hydrochloric acid for 60 min.
CONCLUSIONS: Chemically induced resorption cavities should be used for experimental studies to better imitate clinical conditions. CBCT requirement is still ambiguous for detection of external resorptions, and more experimental and clinical studies are needed.
Keywords: Cone-Beam Computed Tomography, Endodontics, Root Resorption, Humans, Hydrochloric Acid, Reproducibility of Results, Tooth Root
Background
External root resorption (ERR) is a frequently encountered pathology associated with the physiological or pathological degradation of calcified tissues, such as dentin, cementum, and alveolar bone, by destructive cells [1,2]. ERR generally progresses without showing any clinical signs and symptoms; therefore, radiographic evaluations form the basis of diagnosis in clinical practice [3]. ERR can also occur following orthodontic treatment, dental trauma, pulp infections, bleaching, or periodontal disease. Moreover, impacted teeth, cysts, tumors, and pressure of erupting canines applied to lateral incisors can cause ERR [4,5].
Today, conventional films, photostimulated phosphor plates, and charge-coupled device sensors used in intraoral radiography are the most preferred radiological methods for the diagnosis of ERR [6]. All of these methods have been only partially successful in accurately diagnosing ERR, especially when the lesion is on the buccal or lingual aspect of the tooth [6]. Recent studies showed that those lesions less than 0.3 mm in depth and 0.6 mm in diameter are not detected by conventional periapical radiography [8]. Also, ERR cavities that are located on the buccal or lingual surfaces of the roots are more difficult to detect. Additionally, conventional radiographs can show these cavities after 60% to 70% of tooth demineralization. In some cases, the 2-dimensional (2D) nature of these images misleads the accurate decision making because of inaccuracy in diagnosing the location, type, and severity of defects [9]. Accurate and early diagnosis of ERR is very important in designing a treatment plan and predicting the prognosis of treatment. As ERR presents no clinical symptoms, it is generally detected at the advanced stage during radiologic examination with periapical radiography. However, periapical radiography can provide limited information about the correct size, location, and extent of the ERR [10,11].
In addition, it is desired that ultrasound imaging be used as an alternative for the diagnosis of lesions in the periapical region, owing to its advantages, which include not using ionizing radiation and obtaining real-time images. However, although it has been found to be successful in the diagnosis of periapical lesion in the anterior teeth region, the difficulty in obtaining images, especially in the posterior region, owing to the high cortical bone thickness, suggests that the use of ultrasound imaging in this region will be limited [12]. Due to the aforementioned factors, diagnostic radiographic methods, such as 3-dimensional (3D) images, have an important role in dental practice. There are studies evaluating whether MR imaging, which is a noninvasive, 3D imaging method, can also be used in imaging the root and surrounding structures of the tooth [13,14].
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) has been designed to produce the 3D image of dental structures and the maxillofacial skeleton [15]. The main advantages of CBCT include a reduction in radiation exposure, a rapid scan time, and fewer image artifacts [15]. Several studies have confirmed the advantage and accuracy of CBCT in evaluating root resorptions [17–20]. In 2007, Cohenca et al found CBCT to be highly successful in detecting the location and extent of ERRs. Accordingly, they concluded that the correct evaluation before the procedure will contribute to the reduction of the negative effects that will develop after the treatment [21]. In the study conducted by Schröder et al in 2018, periapical radiography images and CBCT images were compared in terms of ERR diagnosis, and CBCT images were found to be much more successful in terms of diagnosis [22]. CBCT units offer voxel sizes ranging from 0.075 to 0.4 mm. Voxel size selection affects scanning, reconstruction time, diagnostic accuracy, and radiation dose [10,23]. It is stated that the smaller the voxel size, the higher the odds of visualization of smaller defects [24].
The goal of this study was to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of CBCT images of chemically induced ERRs on extracted human teeth taken in different voxel sizes. To the best of our knowledge, no previous study to date has compared the accuracy of different CBCT voxel sizes in chemically induced ERR lesions that imitate the real ERR lesions more closely than mechanically created ones. Voxel size is associated with the image quality and radiation dose [17]. In this way, we aimed to find the optimum voxel size to visualize the external resorptions with the least amount of radiation dose to the patient.
Material and Methods
In this in vitro study, 36 maxillary and 36 mandibular human incisor teeth, previously extracted owing to periodontal disease, were used. Teeth without ERR, caries, and restoration were included in the study. Teeth with caries, ERR, or restoration were excluded from the study. The teeth were divided into 12 groups and each group included 6 incisors. The samples were coded to keep the same teeth in the same group for every single scan. External resorption cavities were created on the buccal or proximal surfaces by using 10% hydrochloric acid with different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, which is noted to be used as the criterion standard for radiographic evaluation. An ERR area was created on the buccal or proximal surface of each tooth. To imitate the natural defects more closely, we used chemically induced defects; therefore, the size of the defects were unknown. However, as the etching time increased, the size of the defect increased. However, the measuring of the size of ERR defects was not the scope of our study.
Resorption cavities in different depths were induced to simulate different levels of external resorption. The area where the defect was planned to be created in the teeth was first covered with wax. Then, 2 layers of nail polish, which was not affected by the acid we used, was applied to all surfaces of the teeth. Following this, we removed the wax that we applied before from the relevant area. Thus, other parts of the tooth were isolated from the acid, except for the area where we planned to create resorption. We then obtained CBCT images before the teeth were immersed in the acid bath to monitor whether the integration of the teeth was preserved in later stages. In the next step, we first immersed the teeth in the acid bath for 10 min and then removed them from the acid bath to obtain CBCT images and evaluate these images. Afterward, we performed the same procedure for the same teeth in 30 and 60 min of acid applications. The maxilla and mandible of 3 dry skulls were used to carry and scan the teeth. The teeth were placed in the anterior sockets of the dry jaws. Dry sockets were gently adapted for teeth to place 2 groups of teeth in every single jaw and then the jaws were also coded to carry the same teeth in every single scan. CBCT images were taken with Planmeca Promax 3D Max CBCT (Planmeca, Helsinki, Finland). Images were taken in 4 different voxel sizes, 400 μm, 200 μm, 150 μm and 100 μm, which were available in the device. A 50×55-mm field of view (FOV) size was used, which was available to obtain images in all voxel sizes. The jaws were placed in the CBCT device and positioned according to the head positioning lights. Two-ply modeling waxes were placed buccally and lingually to imitate soft tissues and then the jaws were exposed (Figure 1). After all the images were obtained, one researcher renamed and mixed the images. The researcher performed a randomized data set of CBCT images with the manufacturer’s viewer software (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca, Helsinki, Finland). The images were evaluated by 2 different observers in all sections. The observers used the following 5-point ranking scale to record their level of confidence concerning the absence or presence of external resorption: 1, definitely not present; 2, probably not present; 3, uncertain; 4, probably present; and 5, definitely present.
Two observers determined the randomized CBCT images and they were informed to feel free to use all the display settings of the software as they wished while investigating. All sections were used to evaluate the ERR cavities (Figure 2). The κ statistic was employed to assess intraobserver and interobserver agreement using the NCSS 2007 statistical software package (NCSS and GESS; NCSS, LLC, Kaysville, UT, USA). The κ values were interpreted according to the guidelines of Landis and Koch as follows: κ≤0.20, poor; κ=0.21–0.40, fair; κ=0.41–0.60, moderate; κ=0.61–0.80, good; and κ=0.81–1.00, very good [25]. All evaluations were compared according to the identified criterion standard. Results were considered statistically significant at
Results
Table 1 shows the κ coefficients for the overall interobserver agreement according to voxel size. In this study, we used 4 different voxel sizes. There was no statistically significant difference between interobserver and intraobserver reliability. Higher observer agreement was obtained for voxel sizes of 100 μm and 150 μm.
For detection of ERR defects, the κ coefficient for interobserver agreement was highest for the 100-μm voxel size and when the defects were located on the proximal side of the samples (Table 1).
Regarding the detection of ERR defects after using 10% hydrochloric acid with different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, induced resorption of 10 min could only be seen in the voxel size of 100 μm, while resorption of 60 min could almost be seen in all voxels. Induced resorptions of 60 min in both sides (buccal and proximal) gave the highest accuracy in the detection of ERR (Figure 2).
Table 2 shows the accuracy of the observers’ detection of buccal and proximal resorptions on voxel sized images of 100 μm, 150 μm, 200 μm, and 400 μm, concerning different acid application times. As the voxel sizes increased and the resolution decreased, the ERR detection accuracy of the observers on both buccal and proximal surfaces decreased. Similarly, as the immersion time of the teeth increased and the lesion depth increased, the accuracy of ERR detection of the observers increased. Table 3 shows the κ coefficients for agreement among our observers in assessing the presence of ERR defects after using 10% hydrochloric acid with different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, according to the criterion standard. The highest κ values were obtained for the samples that were kept in hydrochloric acid for 60 min (Figure 2).
Discussion
ERR usually develops without any symptoms and when it is diagnosed, a severe dental tissue loss might result in tooth loss. Thus, early detection of ERR is key to having a successful treatment outcome. Radiographic evaluation is the most important tool for the diagnosis, planning, treatment, and prognosis of ERRs [10]. Only when ERR is detected in the initial stage can the affected tooth be treated by repairing the resorption cavity with no pulpal injury. The detection of ERR in the later stage unfavorably alters the prognosis and might result in root canal treatment or tooth extraction [11,26]. Some researchers have thought of using ERR markers in saliva and gingival cervical fluid as an alternative to traditional methods because they thought that classical radiography methods were insufficient to diagnose ERR in the early stage. Although there have been results showing that ERR markers can be used for diagnosis in moderate and severe resorption, it was thought that these markers could be confused with the physiological remodeling process at the initial level [27]. Similarly, although a study conducted in 2021 showed promising results for the use of some biomarkers in gingival cervical fluid in the diagnosis of ERR, the authors emphasized that more studies are required for their use in clinical conditions. This makes us think that CBCT is the most appropriate diagnostic method that can be used for early ERR diagnosis in order to prevent tooth loss under the current conditions [28]. To the best of our knowledge, there is no 2D imaging technique available to provide an accurate and easy to interpret diagnostic tool for the detection of ERR. A few studies [15,29,30] have compared the diagnostic accuracy between CBCT, digital sensors (charge-coupled device, photostimulable phosphor plates, or complementary metal-oxide semiconductor), and conventional films. Almost all of them showed that CBCT had an accuracy of over 90% in diagnosing external resorption.
Owing to the increased use of CBCT in dentistry, it is crucial to find out which imaging protocol can give 3D images with adequate sharpness and resolution for the detection and measurements of small structures, such as natural ERR lesions. Some CBCT imaging protocols have been proposed for the accurate diagnosis and measurements of ERR lesions produced artificially with a bur [31]. However, while assessing chemically induced ERR, which better mimics natural ERR, the present study showed that the cavities are not as easily visualized and CBCT has low accuracy regarding cavity detection, especially in the buccal region and when the teeth are immersed in the acid for a short time. Although there is a possibility that MR imaging that does not contain ionizing radiation can be used in the detection of ERR, we think that it will not be practical for use in current conditions owing to the need for special equipment and personnel, high cost, and unsuitability for use in the dental clinic setting [13].
Liedke et al [17] reported that higher resolution (0.2-mm and 0.3-mm voxel size) CBCT images showed ERR better than low resolution (0.4-mm3 voxel) images, but with no statistically significant difference (
We assessed the effect of different voxel sizes on the observer’s ability to diagnose ERR by using the smallest available FOV (55×50 mm) in the machine. Different results and observer performance may be obtained when using different FOV and voxel sizes.
Some studies showed that CBCT sections were effective in the detection of ERR. Sonmez et al [10] reported that the sagittal views were more versatile and user-friendly than the axial views to measure ERR size. Likewise, Lermen et al [32] showed that in the diagnosis of small apical ERR lesions (0.3-mm depth and 0.6-mm diameter), the sagittal section was more accurate than others. However, while considering these results, we did not use only the sagittal view to evaluate the images but also used the other views (coronal, axial, and cross-sectional) to be able to evaluate the proximal and buccal surfaces of teeth.
Among the CBCT parameters (tube current, milliamperage setting, detector type, FOV, voxel size, and scanning type) affecting the image quality, voxel size is one of the most important and is closely associated with the scanning and reconstruction time. The voxel size dictates the level of detail in an image, which is its resolution, as well the scanning mode, which determines the number of basis images since it is directly associated with the spatial resolution of the image [23,31]. Therefore, the longer the scan time and the smaller the voxel size, the better the resolution details will be. On the other hand, the use of a small voxel size increases the exposure time which can result in a higher radiation dose, patient movement artifact, and longer reconstruction time [31]. Therefore, to reduce the patient radiation dose, the determination of optimal CBCT protocols is critical. The ideal imaging protocol would be a balance between the minimum radiation exposure and the best resolution achievable [23,31]. Since smaller voxels cause higher radiation doses to the patient, different voxel configurations should be chosen to decrease the radiation exposure based on the indication of each examination [31]. Sonmez et al [10] did not find a significant difference between different voxel sizes (0.075, 0.1, 0.15, and 0.2 mm3) in the determination of the diameter and depth of apical and cervical ERRs. Similarly, Liedke et al [17] reported no significant difference between voxel sizes of 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 mm3 in the detection of ERRs. Conversely, Ponder et al [33] reported that a voxel size of 0.2 mm3 was more accurate than one of 0.4 mm3 to detect the different sizes (1 mm and 1.8 mm) of ERR cavities. Goller-Bulut and Ugur-Aydin [26] also reported that decreased voxel size gave more accurate results in middle and coronal region ERR measurements. However, the authors did not find a significant difference in voxel sizes for the diameter and depth of the apical ERRs. The differences in the abovementioned results might be due to different ERR locations and dimensions, different CBCT machines, voxel size, observer experience, and performance [26]. In the present study, we did not find a statistically significant difference between voxel sizes of 100 μm and 150 μm in diagnosing different ERR defects. Thus, considering the generation of higher noise and radiation dose when a small voxel size with a small FOV is used, CBCT scans performed with a voxel size of 150 μm may be convenient for the detection of ERR when indicated.
Safi et al [9] and Silveria et al [34] reported that FOV size, either large or small, did not affect the imaging accuracy significantly. Silveria et al [34] investigated FOV size and voxel size in internal root resorption and reported that the imaging quality is associated more with the voxel size. Therefore, it may be advisable that, for the same voxel size, a smaller FOV size be chosen, owing to less radiation exposure for the patient and better cost-effectiveness.
In a study done on natural ERR cavities, Schroder et al [31] demonstrated that the proximal surface had the highest number of ERR cavities, followed by the buccal and lingual surfaces. The authors did not find a statistically significant difference between different voxel sizes in the assessment of the ERR location. However, the proximal surface gave the highest true positive values among other surfaces separate from the voxel size used. We found a statistically significant difference between locations, with proximal resorptions detected with higher accuracy than the buccal defects. Our results agree with those of Schroder et al [31]
To date, most studies have used artificial ERR cavities that were only mechanically produced with a bur or both mechanically and chemically produced, and there are just a few studies [23] on the accuracy of CBCT on exclusively chemically induced defects. Chemically induced defects are a closer representation of natural ERR defects. Natural ERR cavities might make an accurate diagnosis challenging. Also, it is not ethical or possible to expose the patient to different CBCT protocols to determine their accuracy or to measure the ERR cavity volume [31]. The first ex vivo study that used natural ERR to determine the accuracy of 3 different CBCTs was done by Schroder et al [31] in 2019. The authors compared the sensitivity and specificity of 3 different CBCT machines in the diagnosis of natural ERR utilizing microtomography as the criterion standard. The results showed that CBCT had a lower sensitivity and specificity for the detection of natural ERR cavities than those presented in previous studies using artificial ERR cavities.
The results of the present study showed that the visibility of chemically induced defects is less than that of mechanically induced defects. Mechanically induced defects have a cutting edge so that they can be more detectable. However, real defects have smooth margins, as do chemically induced defects, making them not easily detectable. Visually, chemically induced ERRs more closely resemble true resorptions than do mechanically induced ERRs. If we consider that the studies in the literature have been mostly conducted with mechanically induced resorptions, then the reason our results are lower than those in the general literature, contrary to expectations, may be that mechanically induced resorptions are detected much more easily with CBCT, owing to their sharp borders.
CBCT images can have artifacts, such as those caused by metallic objects, restorations, and patient motion. In our study, there was no metallic restoration or motion artifact in the area of interest; therefore, observer performance was not affected by these factors. However, a limitation of this study was that artificial ERR cavities are well-defined and sharper with regular edges, which are different from natural ERRs. Although we used chemically induced ERR cavities, which are a closer representation of natural defects, the detection accuracy may be still higher than in in vivo conditions.
Conclusions
For detection of ERR defects, the κ coefficient for the interobserver agreement was highest for the 100-μm voxel size and when the defects were located on the proximal side of the samples. For the detection of ERR defects after using 10% hydrochloric acid with different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, the 10-min induced resorption could only be seen in the 100-μm voxel size, while the 60-min resorption could almost be seen in all voxels. Therefore, as the etching time increases, the ERR can be detected at higher voxel values.
The CBCT requirement is still ambiguous for the detection of external resorptions, and more experimental and clinical studies are needed to better understand whether CBCT has a significant capability of detecting natural resorptions. This will prevent unnecessary patient radiation exposure. Chemically induced resorption cavities should be used for experimental studies to better imitate clinical conditions.
Figures
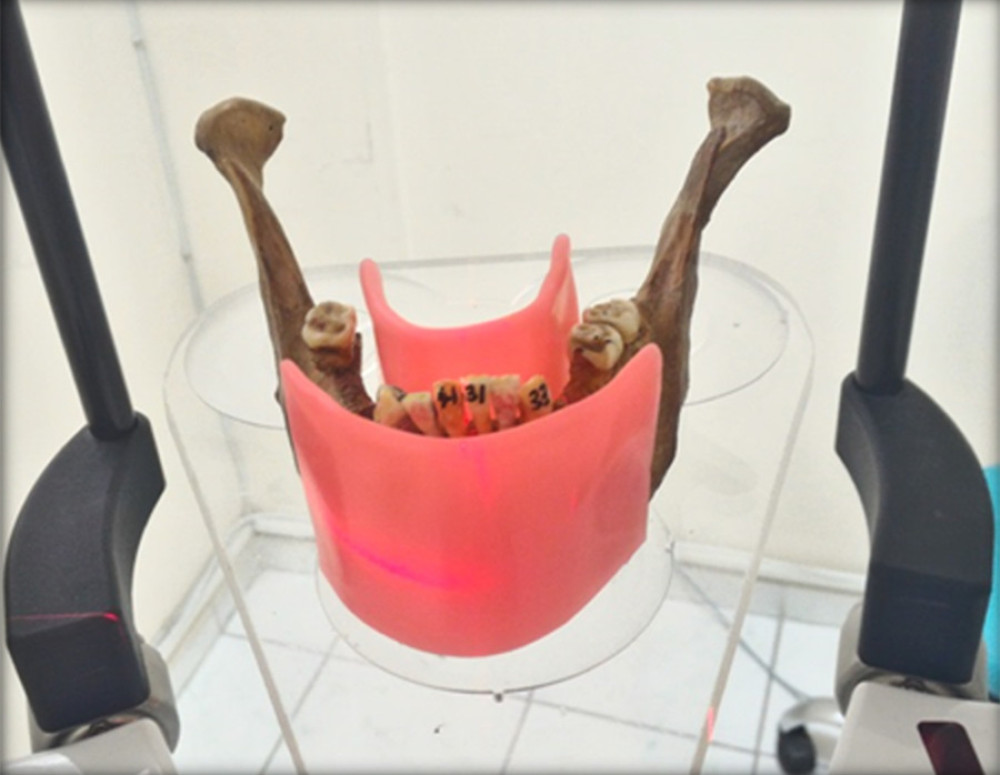 Figure 1. When the CBCT machine became ready to expose, 2-ply modeling waxes were placed buccally and lingually to imitate soft tissues and then the jaws were exposed. (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca.).
Figure 1. When the CBCT machine became ready to expose, 2-ply modeling waxes were placed buccally and lingually to imitate soft tissues and then the jaws were exposed. (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca.). 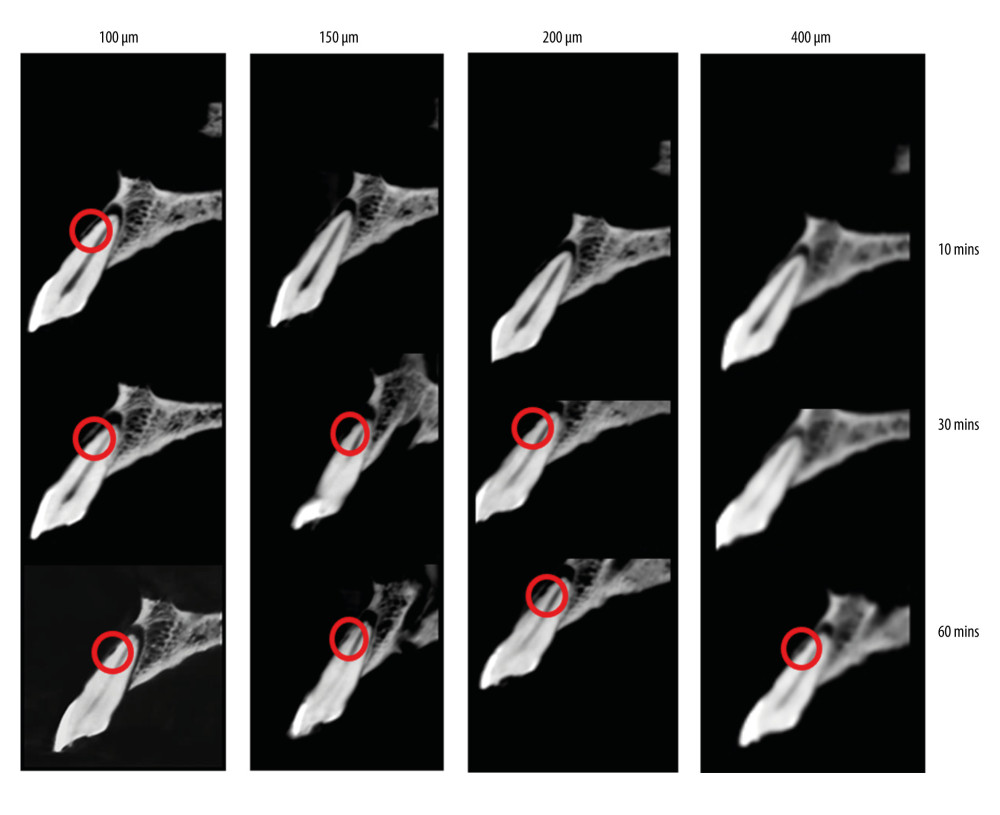 Figure 2. Cross-sectional views in different voxels and different acid bath periods of the same tooth. (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca.).
Figure 2. Cross-sectional views in different voxels and different acid bath periods of the same tooth. (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca.). Tables
Table 1. The κ coefficient for interobserver agreement in the detection of the external root resorption defects.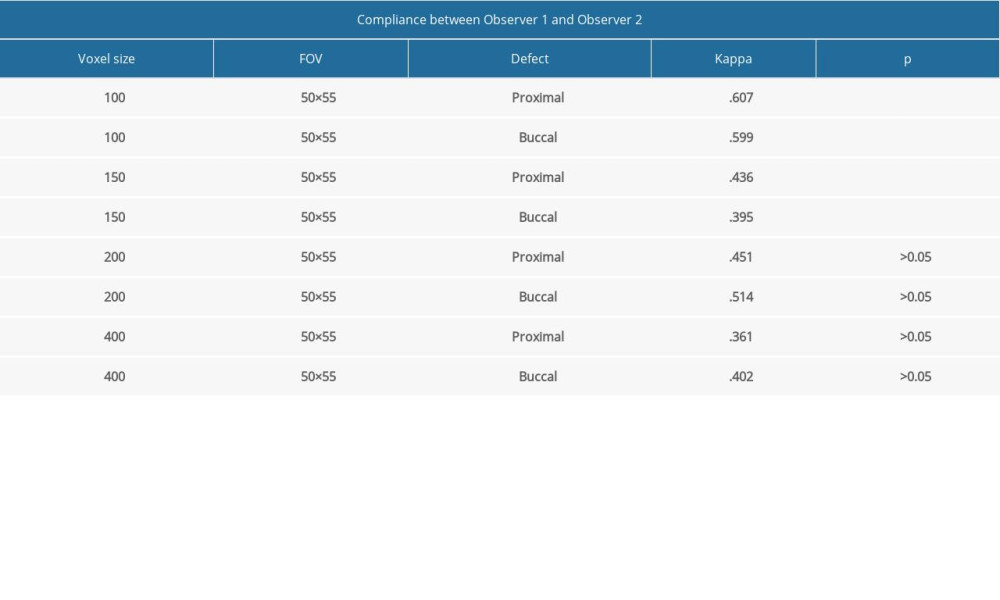 Table 2. Accuracy of observers for detection of buccal and proximal resorptions on different voxel sized images.
Table 2. Accuracy of observers for detection of buccal and proximal resorptions on different voxel sized images.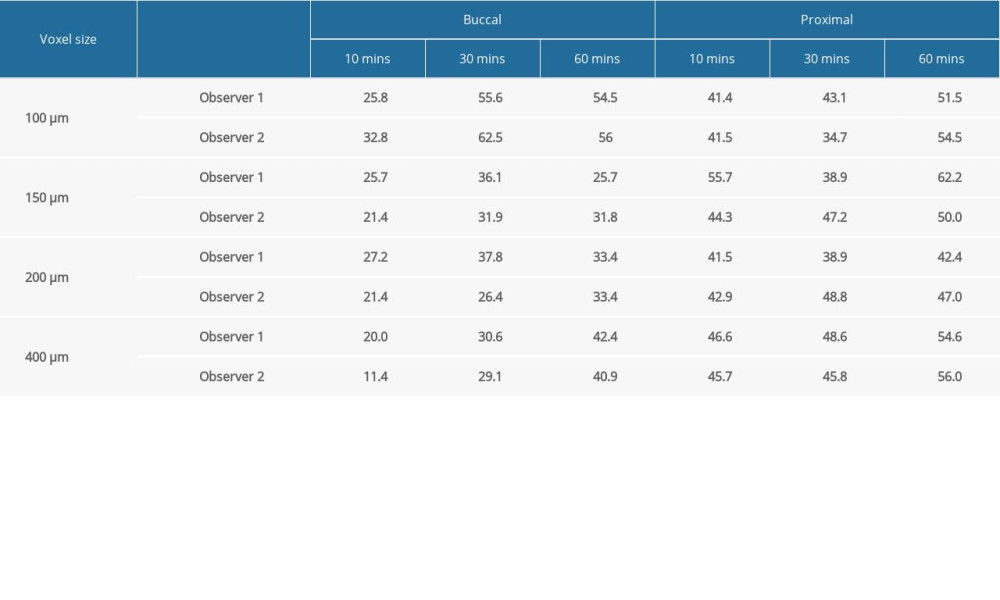 Table 3. The κ coefficients in interobserver agreement for different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, according to the criterion standard.
Table 3. The κ coefficients in interobserver agreement for different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, according to the criterion standard.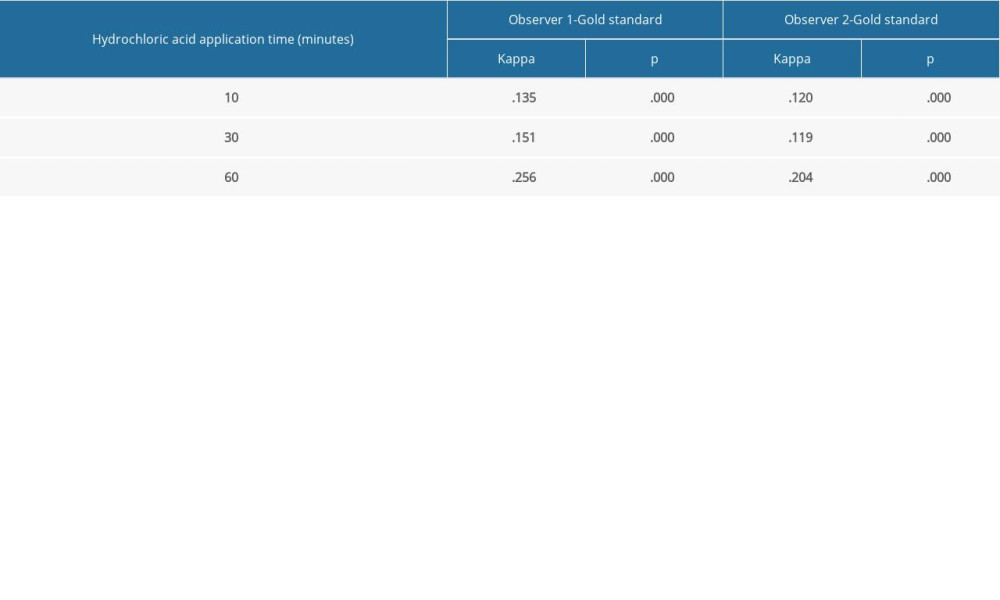
References
1. Shokri A, Mortazavi H, Salemi F, Diagnosis of simulated external root resorption using conventional intraoral film radiography, CCD, PSP, and CBCT: A comparison study: Biomed J, 2013; 36(1); 18-22
2. Ne RF, Witherspoon DE, Gutmann JL, Tooth resorption: Quintessence Int, 1999; 30(1); 9-25
3. Westphalen VP, Gomes de Moraes I, Westphalen FH, Conventional and digital radiographic methods in the detection of simulated external root resorptions: A comparative study: Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2004; 33(4); 233-35
4. Ericson S, Bjerklin K, Falahat B, Does the canine dental follicle cause resorption of permanent incisor roots? A computed tomographic study of erupting maxillary canines: Angle Orthod, 2002; 72(2); 95-104
5. Fuss Z, Tsesis I, Lin S, Root resorption – diagnosis, classification and treatment choices based on stimulation factors: Dent Traumatol, 2003; 19(4); 175-82
6. Andreasen FM, Sewerin I, Mandel U, Andreasen JO, Radiographic assessment of simulated root resorption cavities: Endod Dent Traumatol, 1987; 3(1); 21-27
7. Nance RS, Tyndall D, Levin LG, Trope M, Diagnosis of external root resorption using TACT (tuned aperture computed tomography): Endod Dent Traumatol, 2000; 16(1); 24-28
8. Goldberg F, De Silvio A, Dreyer C, Radiographic assessment of simulated external root resorption cavities in maxillary incisors: Endod Dent Traumatol, 1998; 14(3); 133-36
9. Safi Y, Ghaedsharaf S, Aziz A, Effect of field of view on detection of external root resorption in cone-beam computed tomography: Iran Endod J, 2017; 12(2); 179-84
10. Sönmez G, Koç C, Kamburoğlu K, Accuracy of linear and volumetric measurements of artificial ERR cavities by using CBCT images obtained at 4 different voxel sizes and measured by using 4 different software: An ex vivo research: Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2018; 47(8); 20170325
11. Creanga AG, Geha H, Sankar V, Accuracy of digital periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography in detecting external root resorption: Imaging Sci Dent, 2015; 45(3); 153-58
12. Arslan ZB, Demir H, Berker Yıldız D, Yaşar F, Diagnostic accuracy of panoramic radiography and ultrasonography in detecting periapical lesions using periapical radiography as a gold standard: Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2020; 49(6); 20190290
13. Drăgan OC, Fărcăşanu AŞ, Câmpian RS, Turcu RV, Human tooth and root canal morphology reconstruction using magnetic resonance imaging: Clujul Med, 2016; 89(1); 137-42
14. Juerchott A, Pfefferle T, Flechtenmacher C, Differentiation of periapical granulomas and cysts by using dental MRI: A pilot study: Int J Oral Sci, 2018; 10(2); 17
15. Patel S, Dawood A, Wilson R, The detection and management of root resorption lesions using intraoral radiography and cone beam computed tomography – an in vivo investigation: Int Endod J, 2009; 42(9); 831-38
16. Scarfe WC, Farman AG, Sukovic P, Clinical applications of cone-beam computed tomography in dental practice: J Can Dent Assoc, 2006; 72(1); 75-80
17. Liedke GS, da Silveira HE, da Silveira HL, Influence of voxel size in the diagnostic ability of cone beam tomography to evaluate simulated external root resorption: J Endod, 2009; 35(2); 233-35
18. Hahn W, Fricke-Zech S, Fricke J, Detection and size differentiation of simulated tooth root defects using flat-panel volume computerized tomography (fpVCT): Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod, 2009; 107(2); 272-78
19. Nakata K, Naitoh M, Izumi M, Evaluation of correspondence of dental Computed Tomography imaging to anatomic observation of external root resorption: J Endod, 2009; 35(11); 1594-97
20. Estrela C, Bueno MR, De Alencar AH, Method to evaluate inflammatory root resorption by using cone beam computed tomography: J Endod, 2009; 35(11); 1491-97
21. Cohenca N, Simon JH, Mathur A, Malfaz JM, Clinical indications for digital imaging in dento-alveolar trauma. Part 2: Root resorption: Dent Traumatol, 2007; 23(2); 105-13
22. Deliga Schröder ÂG, Westphalen FH, Schröder JC, Accuracy of digital periapical radiography and cone-beam computed tomography for diagnosis of natural and simulated external root resorption: J Endod, 2018; 44(7); 1151-58
23. Sousa Melo SL, Vasconcelos KF, Holton N, Impact of cone-beam computed tomography scan mode on the diagnostic yield of chemically simulated external root resorption: Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2017; 151(6); 1073-82
24. Nikneshan S, Valizadeh S, Javanmard A, Alibakhshi L, Effect of voxel size on detection of external root resorption defects using cone beam computed tomography: Iran J Radiol, 2016; 13(3); e34985
25. Landis JR, Koch GG, The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data: Biometrics, 1977; 33(1); 159-74
26. Goller Bulut D, Uğur Aydın Z, The impact of different voxels and exposure parameters of CBCT for the assessment of external root resorptions: A phantom study: Aust Endod J, 2019; 45(2); 146-53
27. Balducci L, Ramachandran A, Hao J, Biological markers for evaluation of root resorption: Arch Oral Biol, 2007; 52(3); 203-8
28. Mona M, Abbasi Z, Kobeissy F, A Bioinformatics systems biology analysis of the current oral proteomic biomarkers and implications for diagnosis and treatment of external root resorption: Int J Mol Sci, 2021; 22(6); 3181
29. Durack C, Patel S, Davies J, Diagnostic accuracy of small volume cone beam computed tomography and intraoral periapical radiography for the detection of simulated external inflammatory root resorption: Int Endod J, 2011; 44(2); 136-47
30. D’Addazio PS, Campos CN, Özcan M, A comparative study between cone-beam computed tomography and periapical radiographs in the diagnosis of simulated endodontic complications: Int Endod J, 2011; 44(3); 218-24
31. Deliga Schröder AG, Westphalen FH, Accuracy of different imaging CBCT systems for the detection of natural external radicular resorption cavities: An ex vivo study: J Endod, 2019; 45(6); 761-67
32. Lermen CA, Liedke GS, da Silveira HE, Comparison between two tomographic sections in the diagnosis of external root resorption: J Appl Oral Sci, 2010; 18(3); 303-7
33. Ponder SN, Benavides E, Kapila S, Hatch NE, Quantification of external root resorption by low- vs high-resolution cone-beam computed tomography and periapical radiography: A volumetric and linear analysis: Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2013; 143(1); 77-91
34. Da Silveira PF, Fontana MP, Oliveira HW, CBCT-based volume of simulated root resorption – influence of FOV and voxel size: Int Endod J, 2015; 48(10); 959-65
Figures
 Figure 1. When the CBCT machine became ready to expose, 2-ply modeling waxes were placed buccally and lingually to imitate soft tissues and then the jaws were exposed. (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca.).
Figure 1. When the CBCT machine became ready to expose, 2-ply modeling waxes were placed buccally and lingually to imitate soft tissues and then the jaws were exposed. (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca.). Figure 2. Cross-sectional views in different voxels and different acid bath periods of the same tooth. (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca.).
Figure 2. Cross-sectional views in different voxels and different acid bath periods of the same tooth. (Romexis viewer 3.0.2, Planmeca.). Tables
 Table 1. The κ coefficient for interobserver agreement in the detection of the external root resorption defects.
Table 1. The κ coefficient for interobserver agreement in the detection of the external root resorption defects. Table 2. Accuracy of observers for detection of buccal and proximal resorptions on different voxel sized images.
Table 2. Accuracy of observers for detection of buccal and proximal resorptions on different voxel sized images. Table 3. The κ coefficients in interobserver agreement for different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, according to the criterion standard.
Table 3. The κ coefficients in interobserver agreement for different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, according to the criterion standard. Table 1. The κ coefficient for interobserver agreement in the detection of the external root resorption defects.
Table 1. The κ coefficient for interobserver agreement in the detection of the external root resorption defects. Table 2. Accuracy of observers for detection of buccal and proximal resorptions on different voxel sized images.
Table 2. Accuracy of observers for detection of buccal and proximal resorptions on different voxel sized images. Table 3. The κ coefficients in interobserver agreement for different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, according to the criterion standard.
Table 3. The κ coefficients in interobserver agreement for different application periods of 10, 30, and 60 min, according to the criterion standard. In Press
15 Apr 2024 : Laboratory Research
The Role of Copper-Induced M2 Macrophage Polarization in Protecting Cartilage Matrix in OsteoarthritisMed Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943738
07 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Knowledge of and Attitudes Toward Clinical Trials: A Questionnaire-Based Study of 179 Male Third- and Fourt...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943468
08 Mar 2024 : Animal Research
Modification of Experimental Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) in Rat Pups by Single Exposure to Hyp...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943443
18 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparative Analysis of Open and Closed Sphincterotomy for the Treatment of Chronic Anal Fissure: Safety an...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944127
Most Viewed Current Articles
17 Jan 2024 : Review article
Vaccination Guidelines for Pregnant Women: Addressing COVID-19 and the Omicron VariantDOI :10.12659/MSM.942799
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942799
14 Dec 2022 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variability of Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin E in Patients with Elevated Tryptase LevelsDOI :10.12659/MSM.937990
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e937990
16 May 2023 : Clinical Research
Electrophysiological Testing for an Auditory Processing Disorder and Reading Performance in 54 School Stude...DOI :10.12659/MSM.940387
Med Sci Monit 2023; 29:e940387
01 Jan 2022 : Editorial
Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Pa...DOI :10.12659/MSM.935952
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935952








