18 October 2020: Animal Study
Silencing of Long Non-Coding RNA X Inactive Specific Transcript (Xist) Contributes to Suppression of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Induced by Hyperoxia in Newborn Mice via microRNA-101-3p and the transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1)/Smad3 Axis
Wenhao Yuan 1ABCDEF* , Xiaoyan Liu 1ABCDG* , Lingkong Zeng 1BCDFG* , Hanchu Liu 1ABCDEFG , Baohuan Cai 2ABCDEFG , Yanping Huang 1ABDF , Xuwei Tao 1ABCDF , Luxia Mo 1ABDF , Lingxia Zhao 1BCDF , Chunfang Gao 1BCDFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.922424
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e922424
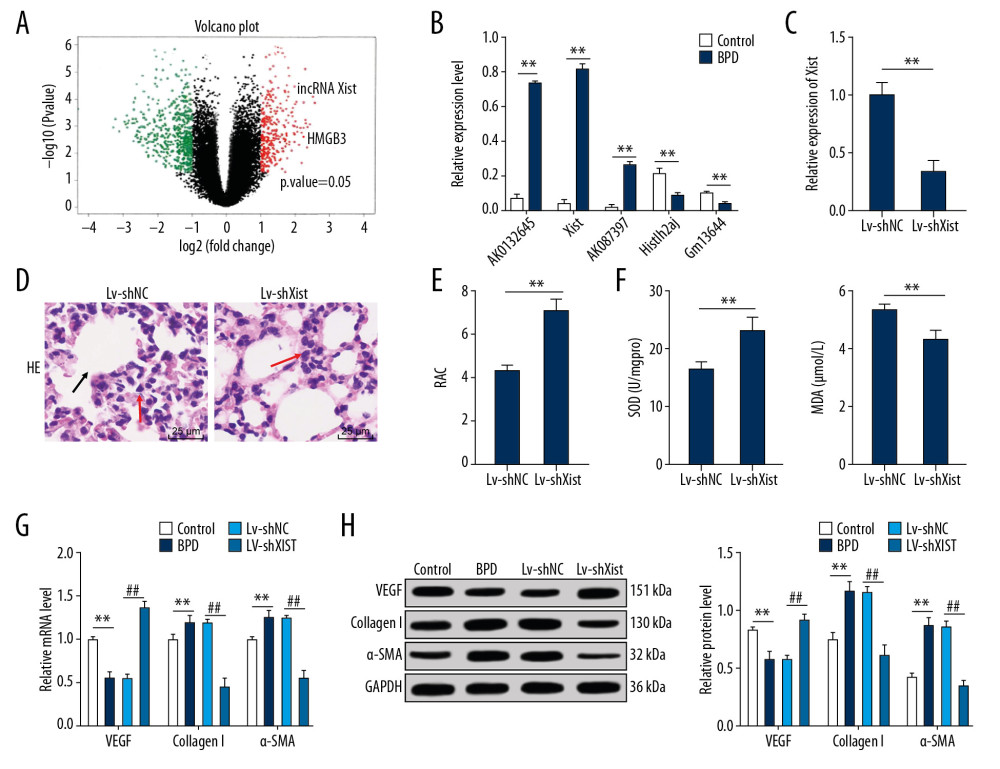
Figure 2 Silenced Xist alleviated lung damage in newborn BPD mice. (A) There was a significantly different fold change in lncRNA expressions between the control group and the BPD group. (B) RT-qPCR showed that the Xist expression was clearly higher in BPD mice than in control mice, n=3. (C) RT-qPCR showed that Xist expression in BPD group was evidently lower than that in the control group with silenced Xist, n=3. (D) HE staining suggested that the lung tissue structure in BPD mice was improved when Xist expression was silenced, with the black arrows indicating alveolar fusion and the red ones indicating alveolar septum, ×400, n=5. (E) RAC in BPD mice increased with silenced Xist, n=5. (F) ELISA showed that SOD activity was increased while MDA level was decreased in BPD mice with silenced Xist, n=3. (G, H) RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis showed that VEGF mRNA and protein expression levels were reduced while mRNA and protein expression levels of collagen I and α-SMA were increased, n=3. Two-way ANOVA was applied to assess data in panels B, G, and H. Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was used for post hoc test. The t test was used for analyzing data in remaining panels. ** p<0.01, ## p<0.01. Xist – X inactive specific transcript; BPD – bronchopulmonary dysplasia; RT-qPCR – reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; HE – hematoxylin-eosin; RAC – radial alveolar counts; SOD – superoxide dismutase; MDA – malondialdehyde; VEGF – vascular endothelial growth factor; α-SMA – alpha-smooth muscle Actin; ANOVA – analysis of variance.


