18 October 2020: Animal Study
Silencing of Long Non-Coding RNA X Inactive Specific Transcript (Xist) Contributes to Suppression of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Induced by Hyperoxia in Newborn Mice via microRNA-101-3p and the transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1)/Smad3 Axis
Wenhao Yuan 1ABCDEF* , Xiaoyan Liu 1ABCDG* , Lingkong Zeng 1BCDFG* , Hanchu Liu 1ABCDEFG , Baohuan Cai 2ABCDEFG , Yanping Huang 1ABDF , Xuwei Tao 1ABCDF , Luxia Mo 1ABDF , Lingxia Zhao 1BCDF , Chunfang Gao 1BCDFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.922424
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e922424
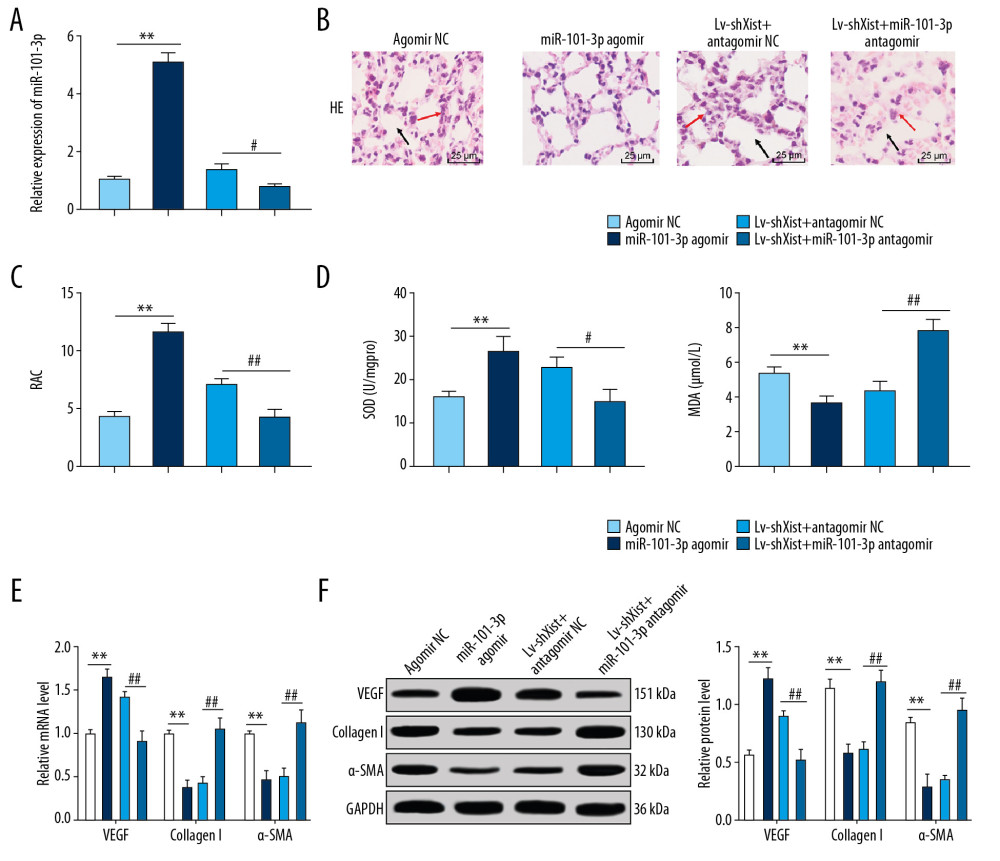
Figure 4 Overexpressed miR-101-3p mitigated lung damage in newborn BPD mice. (A) RT-qPCR showed silencing miR-101-3p in lung tissues reduced miR-101-3p expression in BPD mice, n=3. (B) HE staining indicated the structural changes in lung tissues of BPD mice after silencing miR-101-3p, with the black arrows indicating alveolar fusion and the red ones indicating alveolar septum, ×400, n=5. (C) RAC was enhanced when miR-101-3p was overexpressed, n=5. (D) ELISA showed improved SOD activity and decreased MDA level with overexpressed miR-101-3p, n=3. (E, F) RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis suggested that mRNA expression and protein level in VEGF were enhanced while those in collagen I and α-SMA were reduced, n=3. Two-way ANOVA was applied to assess data in panels E, F, and one-way ANOVA was applied to assess data in panels A, C, and D. Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was applied for post hoc test. The t test was used for analyzing data in remaining panels. ** p<0.01, ## p<0.01. miR – microRNA; BPD – bronchopulmonary dysplasia; RT-qPCR – reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction; HE – hematoxylin-eosin; RAC – radial alveolar counts; SOD – superoxide dismutase; MDA – malondialdehyde; VEGF – vascular endothelial growth factor; α-SMA – alpha-smooth muscle Actin; ANOVA – analysis of variance.


