30 August 2020: Animal Study
Promoting Role of Long Non-Coding RNA Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 15 (SNHG15) in Neuronal Injury Following Ischemic Stroke via the MicroRNA-18a/CXC Chemokine Ligand 13 (CXCL13)/ERK/MEK Axis
Tiezhu Guo 1AB , Yueting Liu 2CE , Xinliang Ren 1DE , Wei Wang 1EF , Hanrui Liu 3F*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.923610
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e923610
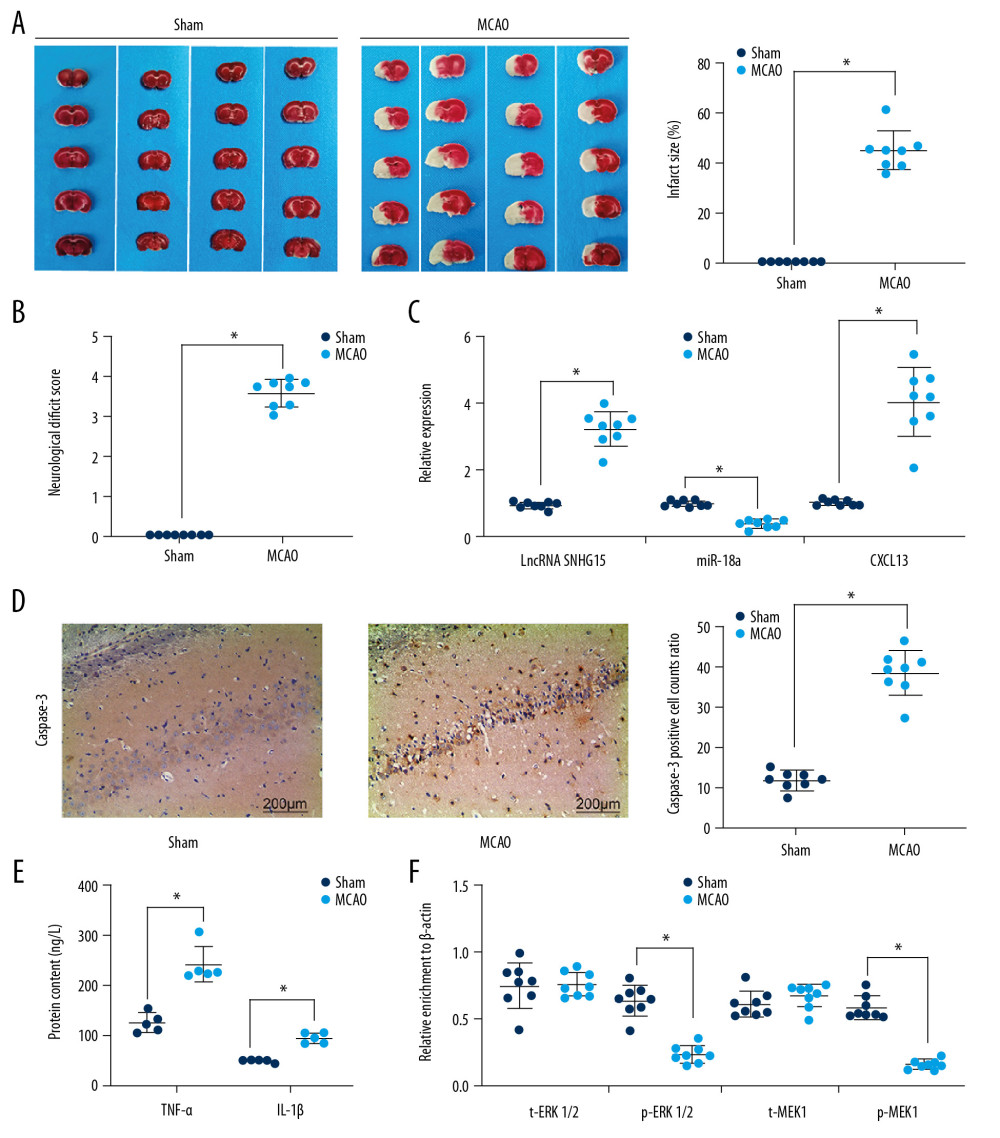
Figure 1 Altered gene expression in mice following MCAO procedures. Model mice were subjected to MCAO with 2 h of ischemia and 24 h of reperfusion, while sham-operated mice underwent the same procedures without ischemia, and then the brains of all mice were collected for the following experiments. (A) Representative images of mouse brain tissue sections after TTC staining. (B) Evaluation of the neurological deficit scores. (C) Expression of SNHG15, miR-18a, and CXCL13 in mouse brain tissues was detected using RT-qPCR. (D) Caspase-3 expression in mouse hippocampal tissues was evaluated using immunohistochemistry staining. (E) Protein levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β in mouse brain were determined using ELISA kits. (F) Contents of total MEK/MRK and phosphorylated MEK/MRK in mouse brain tissues was detected using ELISA kits. Data are shown as mean±SD based on 3 independent experiments. N=8, * p<0.05. In panels A, B, and D, data were analyzed using the unpaired t test, while data in panels C, E, and F were analyzed using one-way ANOVA.


