11 August 2020: Review Articles
Current Status of Research on the Role of Circular RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Clinical Implications
Ren-Chao Zou 1E* , Ling-Lin Li 23CDE* , Hong-Ling Yuan 2A*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.923832
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e923832
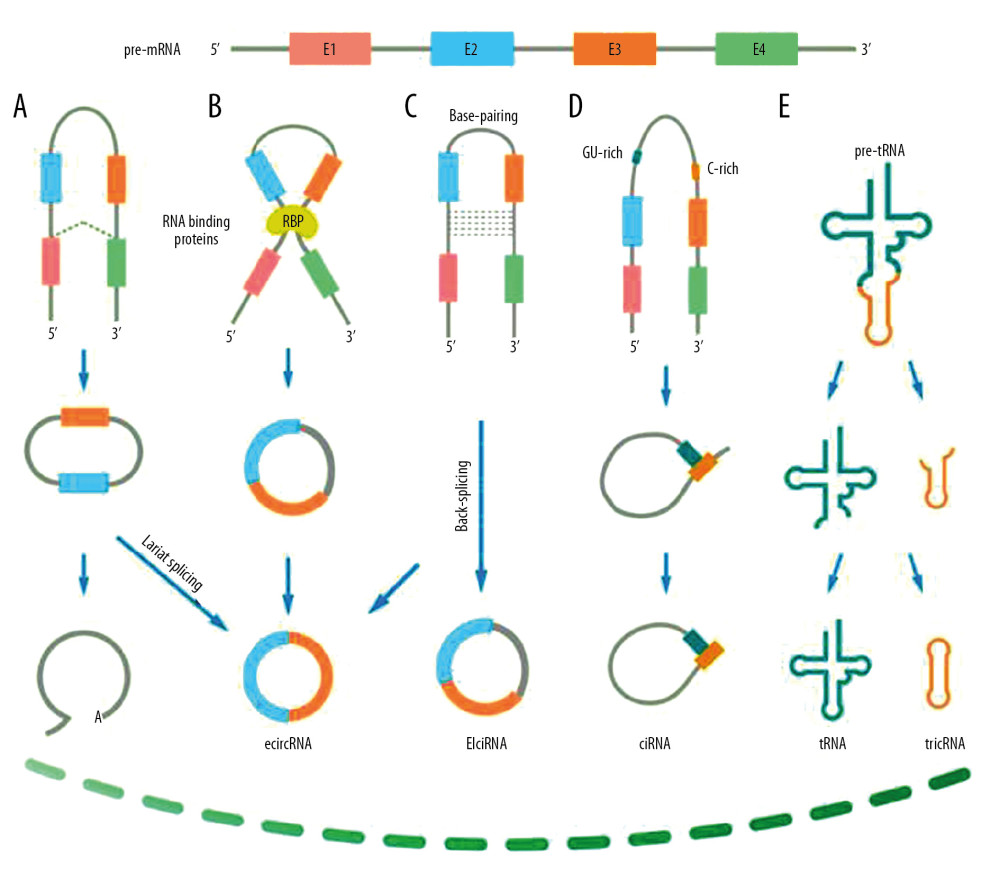
Figure 1 Biogenesis of circular RNAs [23]. (A) Lariat-driven circularization. The 3′ hydroxyl of the upstream exon reacts with the 5′ phosphate of the downstream exon to form a covalent linkage, then producing a lariat including exons and introns. The 2′ hydroxyl of the 5′ intron interacts with the 5′ phosphate of the 3′-intron to form an ecircRNA following an interaction between the 3′ hydroxyl of the 3′ exon and the 5′ phosphate of the 5′ exon. (B) RNA-binding protein (RBP)-driven circularization. RBPs accelerate interaction of the downstream intron and upstream intron, thereby promoting formation of ecircRNA. (C) Base-pairing-driven circularization. The downstream introns and upstream introns are paired depends on inverse-repeating/complementary sequences. Formation of ecircRNA/EIciRNA was derived from the introns are removed/retained. (D) Biosynthesis of ciRNA. Formation of ciRNAs mainly based on a 7-nt GU-rich element and an 11-nt C-rich element to escape debranching and exonucleolytic degradation. (E) Formation of tricRNA. tRNA splicing enzymes divide pre-tRNA into two parts: TricRNAs are generated by a 3′–5′ phosphodiester bond and the other part generates tRNAs.


