07 July 2020: Lab/In Vitro Research
Chlamydial-Secreted Protease Chlamydia High Temperature Requirement Protein A (cHtrA) Degrades Human Cathelicidin LL-37 and Suppresses Its Anti-Chlamydial Activity
Xiaohua Dong 1AB* , Wanxing Zhang 2CE* , Jianmei Hou 3DF , Miaomiao Ma 2DF , Congzhong Zhu 4DF , Huiping Wang 2AG , Shuping Hou 2AG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.923909
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e923909
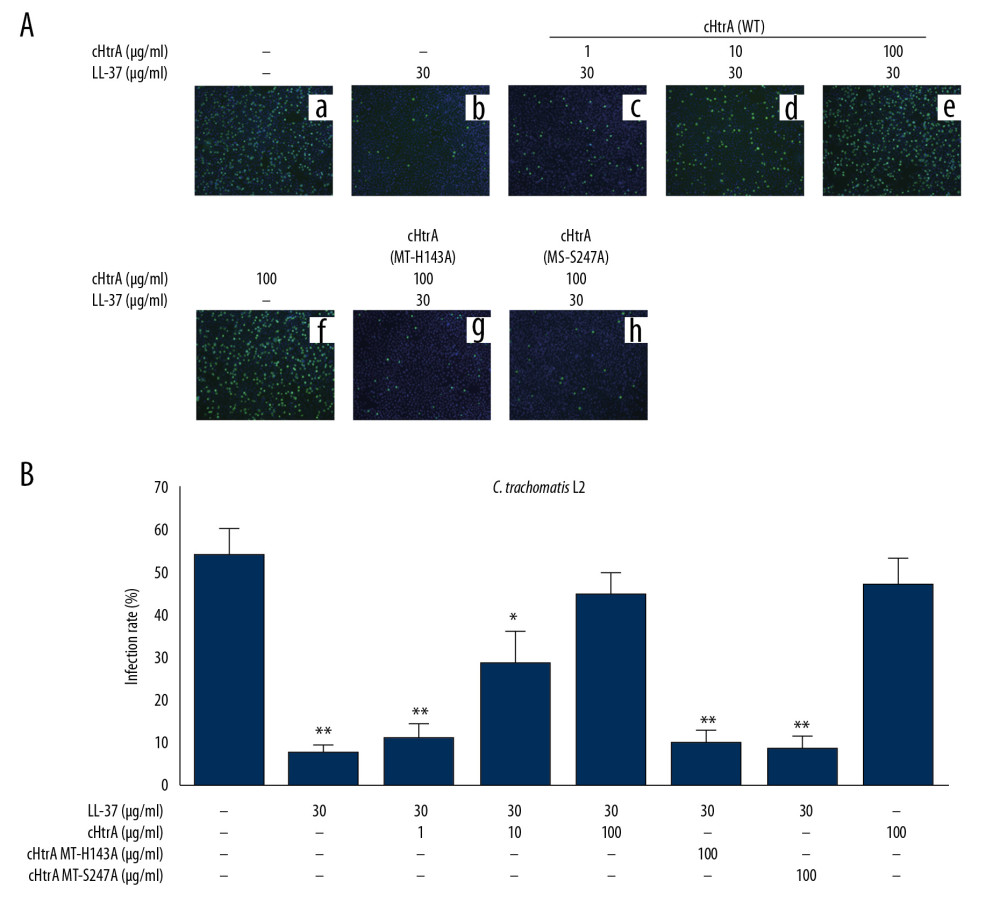
Figure 4 cHtrA blocks the anti-chlamydial effect of LL-37 on C. trachomatis serovar L2. (A) C. trachomatis L2 infection (a) was compared with the effect of LL-37 (30 μg/mL) pre-incubated alone (b), or with 1 (c), 10 (d), or 100 μg/mL (e) wild-type (WT) cHtrA, or 100 μg/mL of MT-H143A (g) or MT-S247A (h) prior to LL-37 treatment of chlamydial organisms. 100 μg/mL of WT cHtrA incubated alone (f) was used as a control to investigate its effect on chlamydial infectivity. As shown in the figure, the C. trachomatis L2 infection (a) was strongly inhibited by 30 μg/mL of LL-37 (b), which was then successfully reversed by pre-incubation of LL-37 with WT cHtrA (c–e) but not mutants (g, h). Five random views per coverslip were counted, and the infection rates are expressed as the mean±SD. Three duplicates were performed for each test. cHtrA concentrations above 30 μg/mL apparently block the anti-chlamydial activity of LL-37. (B) Quantitative data obtained from this experiment. The colors of the tubes represent different experiment operates, and the details are contained in the legends. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01.


