04 September 2020: Animal Study
Individualized Running Wheel System with a Dynamically Adjustable Exercise Area and Speed for Rats Following Ischemic Stroke
Yu-Lin Wang 123ABC , Jui-Chi Cheng 4AB , Ching-Ping Chang 5BCDE , Fong-Chin Su 1EF* , Chi-Chun Chen 4ABDEFG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.924411
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e924411
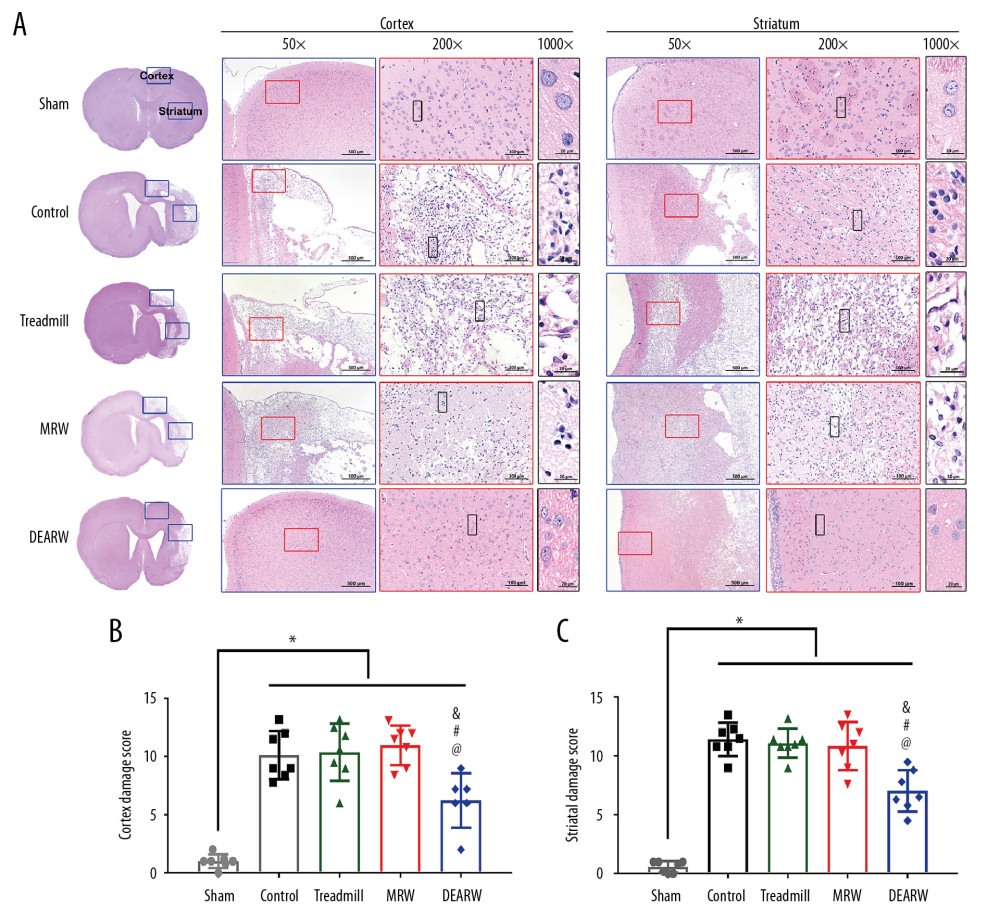
Figure 9 (A) H&E-stained coronal slices illustrating the extent of damage to different parts of the ipsilateral brains of the groups of rats 28 days following middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) or sham surgery. Framed boxes indicate representative areas of peri-infarct cortex and striatum. Sham rats exhibited healthy brain tissue and neuron morphology. MCAO induced severe structural disorganization and moderate levels of pyknotic cells in the cortex and striatum. The dynamic exercise area running wheel (DEARW) treatment attenuated these changes in cell morphology. Brain damage scores in (B) the cortex and (C) the striatum showed that DEARW treatment significantly reduced the cortical and striatal damage scores. Bars represent the means±standard deviations of ten rats. * p<0.05 compared with the sham group; @ p<0.05 compared with the control group; # p<0.05 compared with the treadmill group; & p<0.05 compared with the motorized running wheel group.


