09 August 2020: Lab/In Vitro Research
Dishevelled Associated Activator Of Morphogenesis (DAAM) Facilitates Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Upregulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α (HIF-1α) Expression
Xiaoxu Fang 1B* , Dandan Zhang 2CD* , Wei Zhao 3CD , Longfei Gao 4DE , Lanping Wang 5ABCDEF*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.924670
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e924670
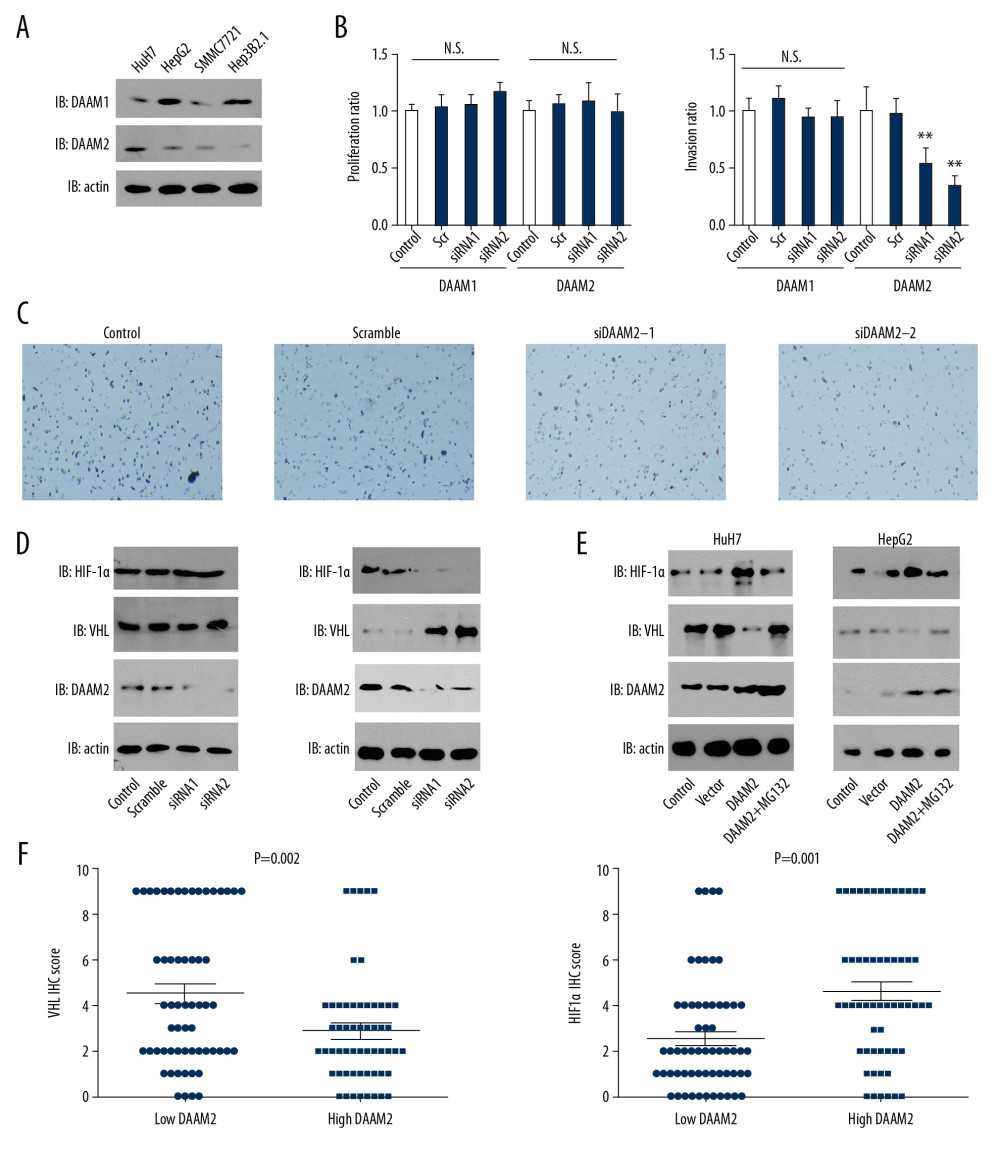
Figure 3 DAAM2 decreased VHL and up-regulated HIF-1α in a ubiquitin-dependent pathway. (A) Expressions of DAAM1 and DAAM2 in different HCC cell lines. (B) Cell proliferation (left) and invasion (right) were detected with MTT assay and transwell assay, respectively, after silencing DAAM1 or DAAM2 expression by siRNA. DAAM1 was silenced in HepG2 while DAAM2 was knocked down in HuH7. N.s. represented not significant and ** meant P<0.01 compared with the control group. (C) Representative images of HuH7 cells transfected with scrambled siRNA, siDAAM2-1 and siDAAM2-2 in transwell assay. (D) Expression of VHL and HIF-1α was detected with Western blot 48 hr after knocking down DAAM1 or DAAM2. DAAM1 was silenced in HepG2 while DAAM2 was knocked down in HuH7 (E). In HuH7 and HepG2, expression of VHL and HIF-1α was detected 48 hr after transfection of empty vector or plasmid carrying DAAM2, in the presence or absence of 10 μM G132 for 6 hr. (F) In the 117 patients with HCC, patients with high DAAM2 expression had lower VHL IHC score and higher HIF-1α IHC score.


