07 August 2020: Lab/In Vitro Research
Reelin Promotes Cisplatin Resistance by Induction of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition via p38/GSK3β/Snail Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Ji-Min Li 1ABCE* , Fang Yang 1C* , Juan Li 2C , Wei-Qi Yuan 1D , Hao Wang 1BG , Yi-Qin Luo 1DG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.925298
Med Sci Monit 2020; 26:e925298
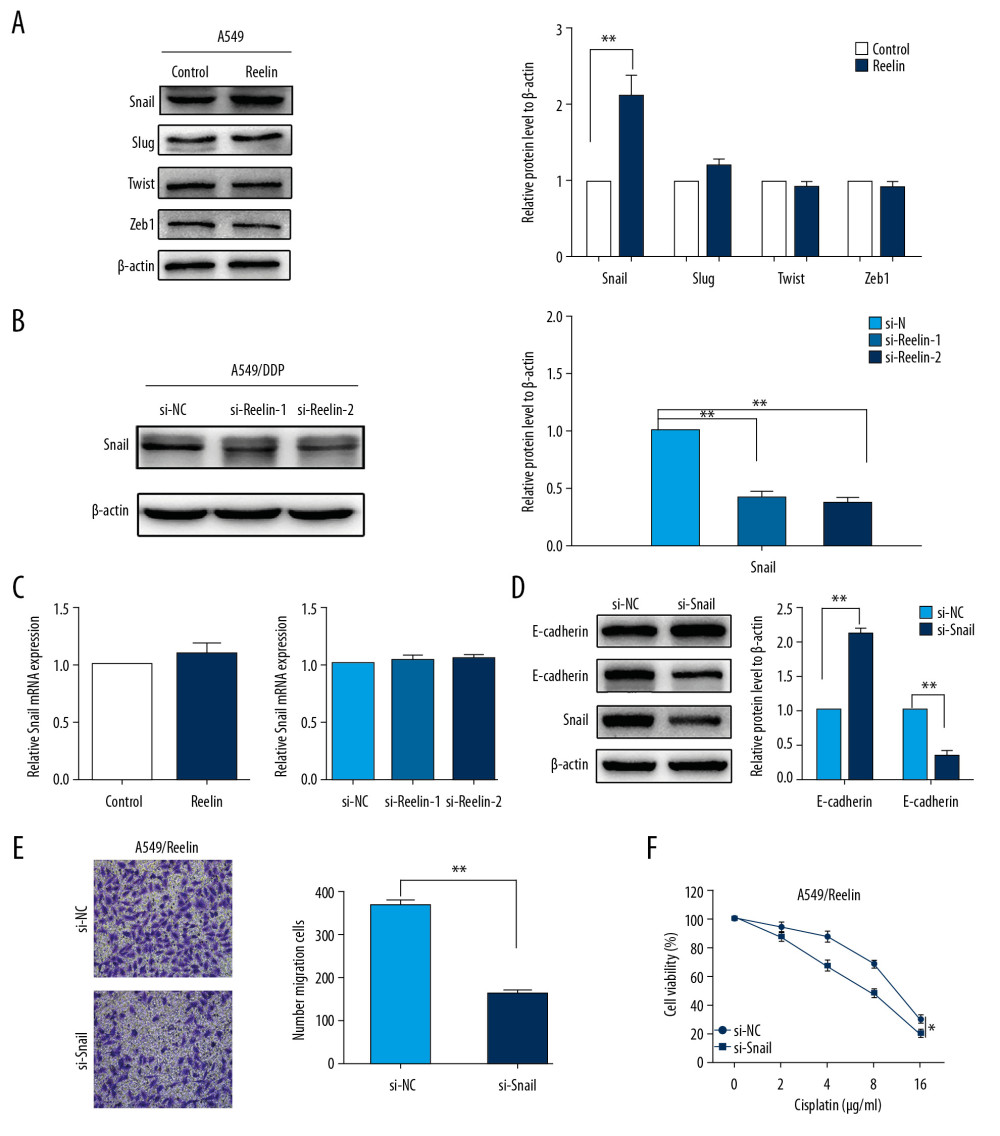
Figure 4 Silencing of Snail reverses the EMT phenotype and cisplatin resistance in NSCLC cells. (A) Effects of Reelin on Snail, ZEB1, Slug, and Twist expression in A549 cells were examined by western blotting. (B) Effects of Reelin on Snail expression in A549/DDP cells were examined by western blotting. (C) Snail expression were evaluated by qRT-PCR in A549 cells transfected with the Reelin expression vector and A549/DDP cells transfected with Reelin si-RNA. (D) The expressions of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and Snail were evaluated by western blotting after Snail knockdown in A549/Reelin cells. (E) Transwell assays revealed dramatically increased migration ability of A549/Reelin cells transfected with si-Snail relative to those transfected with si-NC. (F) A549/Reelin cells were transfected with Snail siRNA, treated with cisplatin at the indicated concentrations for 48 hours, and measured for cell viability by CCK-8 assays. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01. CCK-8 – Cell Counting Kit-8.


