14 April 2021: Animal Study
Zi Qi Decoction Alleviates Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4)-Related Nuclear Factor kappa b (NF-κB) and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Signaling Pathways
Jingwen Zhou 1ABCE* , Xiaolong Zhang 1A* , Lingfeng Wan 1AD , Jun Yu 2BCD , Tianci Li 2BCD , Ziyu Lu 3BCD , Nanyuan Fang 1E , Lixia Sun 1AG* , Fang Ye 2AG*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.929438
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e929438
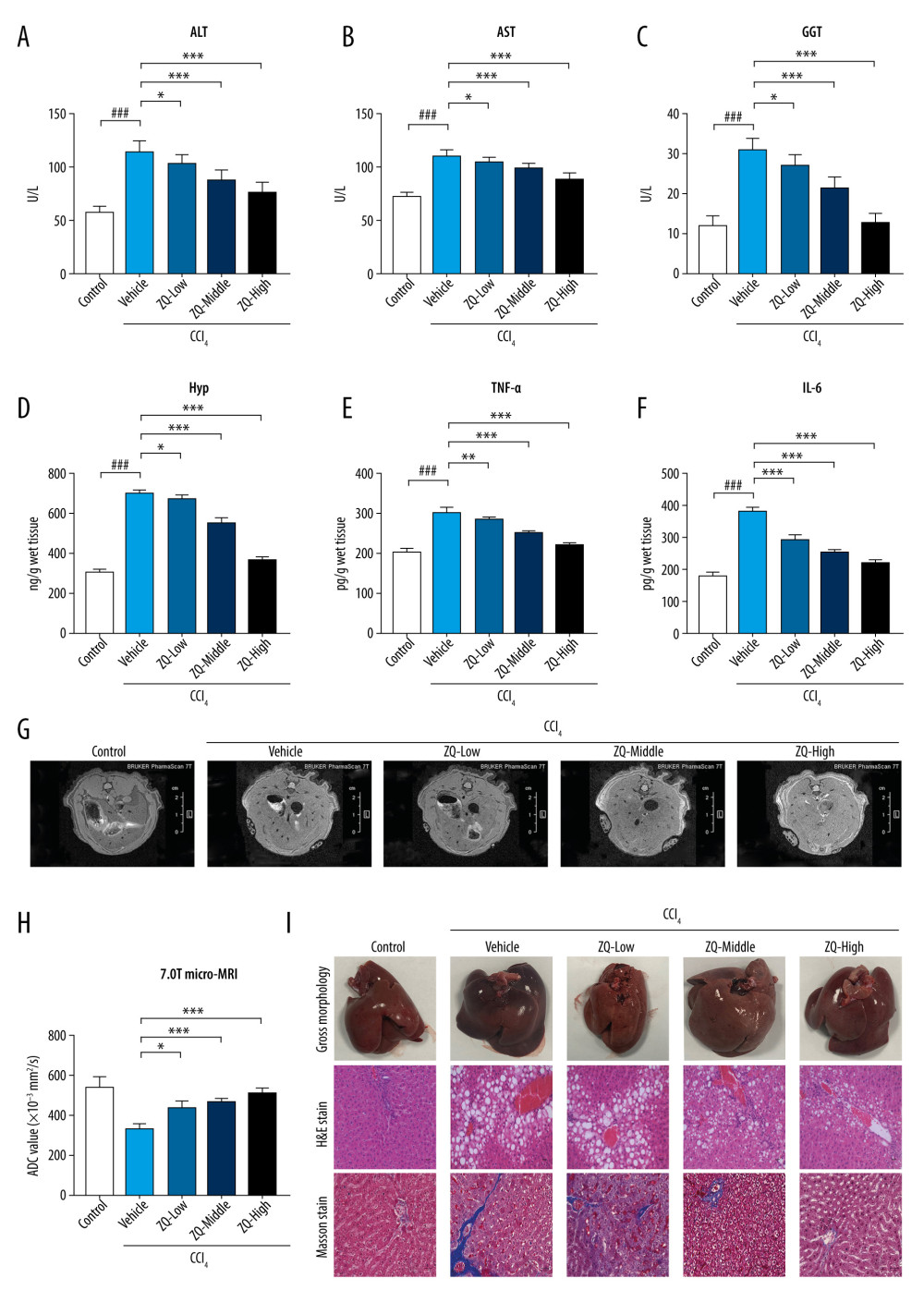
Figure 3 Representative indicators associated with liver fibrosis and Zi Qi decoction effects on macroscopic and microscopic hepatic architecture in CCl4-induced rats. The content of (A) alanine aminotransferase, (B) aspartate aminotransferase, (C) gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, (D) Hyp, (E) tumor necrosis factor-α, and (F) interleukin-6 in each group were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (G) 7.0T micro-magnetic resonance imaging (micro-MRI) was used to evaluate the severity of hepatic damage of rats. (H) Apparent diffusion coefficient values of each slice of micro-MRI in each group when b value=50 s/mm2. (I) Representative images of macroscopic features (upper panel), hematoxylin & eosin staining (middle panel), and Masson staining (lower panel) of liver tissue from rats with hepatic fibrosis. Magnification ×200. ### P<0.001, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001, for comparison with the vehicle group. Data were presented as means±standard deviations.


