25 April 2021: Clinical Research
Predicting the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) or Cardiopulmonary Bypass (CPB) Surgery: Development and Assessment of a Nomogram Prediction Model
Yi Du ABCDEFG , Xiu-Zhe Wang ABFG , Wei-Dong Wu ABCDE* , Hai-Peng Shi ABC , Xiao-Jing Yang CD , Wen-Jing Wu BC , Shu-Xian Chen EFDOI: 10.12659/MSM.929791
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e929791
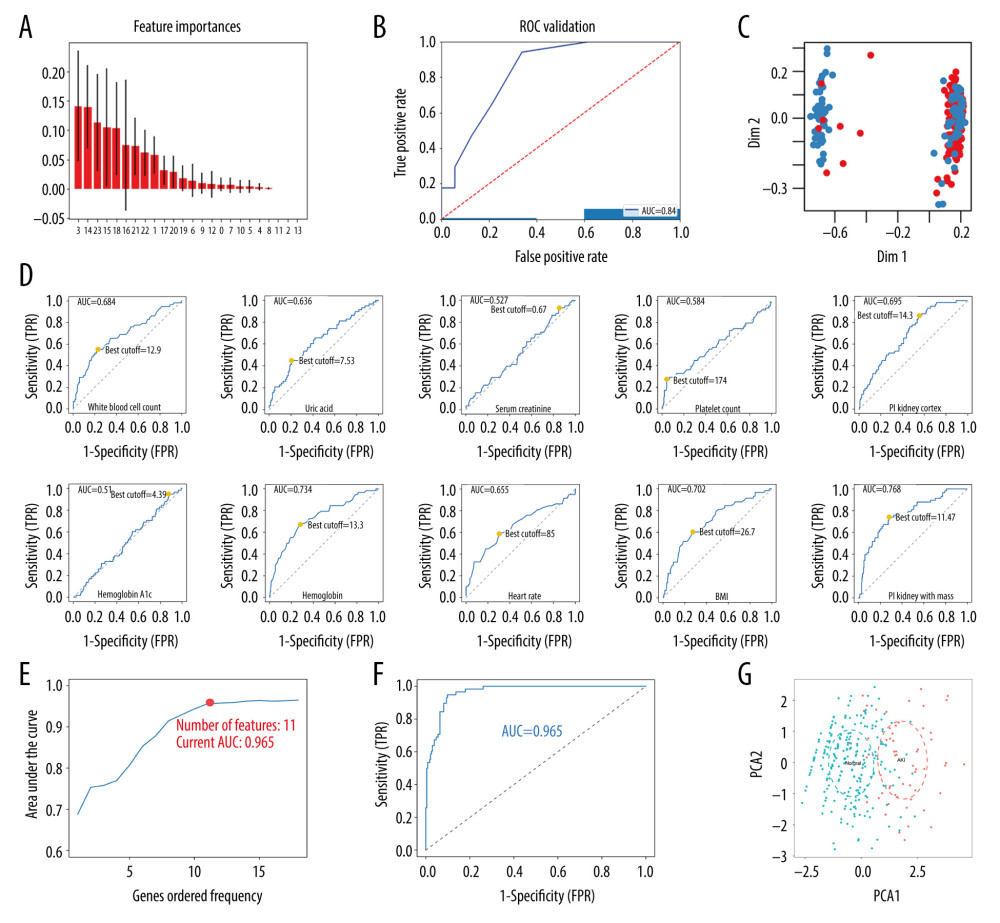
Figure 1 Screening for prediction factors. (A) Importance values of each factor in the random forest model. (B) The ROC curve (AUC=0.84) demonstrated the accuracy of the random forest model. (C) Random forest analysis generated a multidimensional scale map of the matrix. The blue dot represents the normal group and the red dot represents the AKI group. (D) The best cutoff points for the continuous variables. (E) According to the number of times the factors occurred, they were included in the logistic model and the pattern diagram of the AUC value was obtained. Eventually, it was evident that the simplest predictive model with a good predictive ability with only 11 predictive factors could be constructed. (F) The ROC curve (AUC=0.965) demonstrates the accuracy of the logistic model. (G) PCA reveals that those factors selected by the LASSO method could be divided into 2 parts. This indicated that the factors had relatively unique prognostic properties in AKI after cardiac surgery (including CPB and PCI). AKI – acute kidney injury; AUC – area under the curve; CPB – cardiopulmonary bypass; LASSO – least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; PCA – principal component analysis; PCI – percutaneous coronary intervention; ROC – receiver-operating characteristic


