10 August 2021: Clinical Research
A Novel Substrate-Inspired Fluorescence-Based Albumin Detection Improves Assessment of Clinical Outcomes in Hemodialysis Patients Receiving a Nursing Nutrition Intervention
Lei You ABCE* , Xia Wang BDEG* , Wenhong Wang DEF*DOI: 10.12659/MSM.930257
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e930257
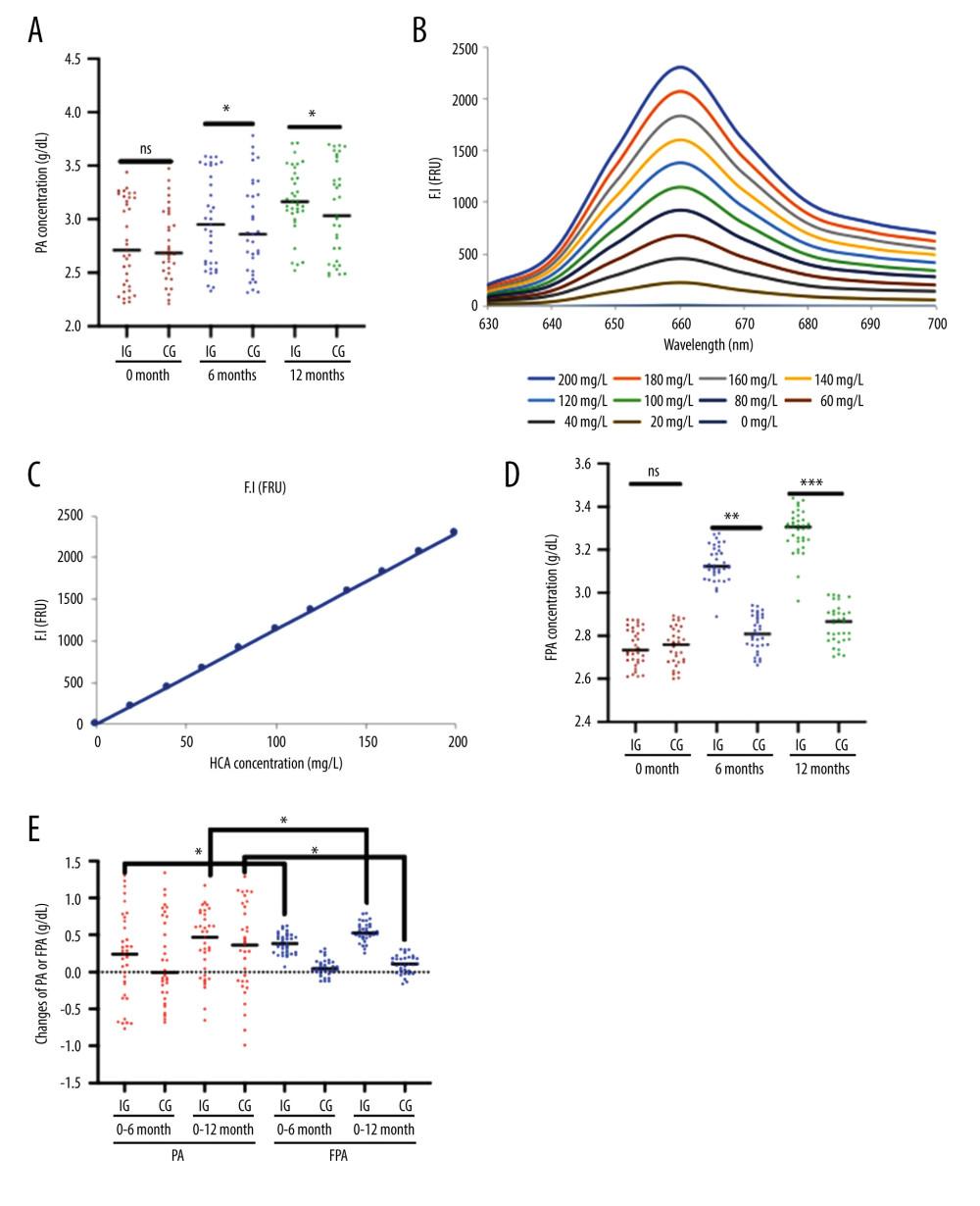
Figure 2 Plasma levels of albumin measured using ELISA (PA) and albumin measured using fluorescent probe (FPA) between the 2 groups. (A) PA concentration (* P<0.05 vs the IG group). (B) The fluorescent profile of DDAMBB probes mixing with different concentrations of human albumin. As the concentration of human albumin increased, the PFA increased and showed the highest value at 662 nm. (C) The linear relationship between the concentrations of human albumin and fluorescent intensity. (D) FPA concentration (** P<0.01 and *** P<0.001 vs the IG group). (E) Changes in PA and PFA concentration (g/dl) from 0 to 6 months and 12 months of intervention (* P<0.05 vs PA). The hemolysis patients were divided into either the Control Group (CG, n=35) or the Intervention Group (IG, n=33). The IG received nutritional supplementation, and the CG group received routine nutritional support. The statistical difference was insignificant for ns between the 2 groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 and *** P<0.001 vs the IG group.


