23 April 2022: Clinical Research
Combining Magnetic Resonance Diffusion-Weighted Imaging with Prostate-Specific Antigen to Differentiate Between Malignant and Benign Prostate Lesions
Liying Han 1CEF , Guanyong He 1CDE , Yingjie Mei 2CD , Qing Yu 3BF , Minning Zhao 3BF , Fu Luo 4B , Guanxun Cheng 1AEG** , Wen Liang 3AE**DOI: 10.12659/MSM.935307
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935307
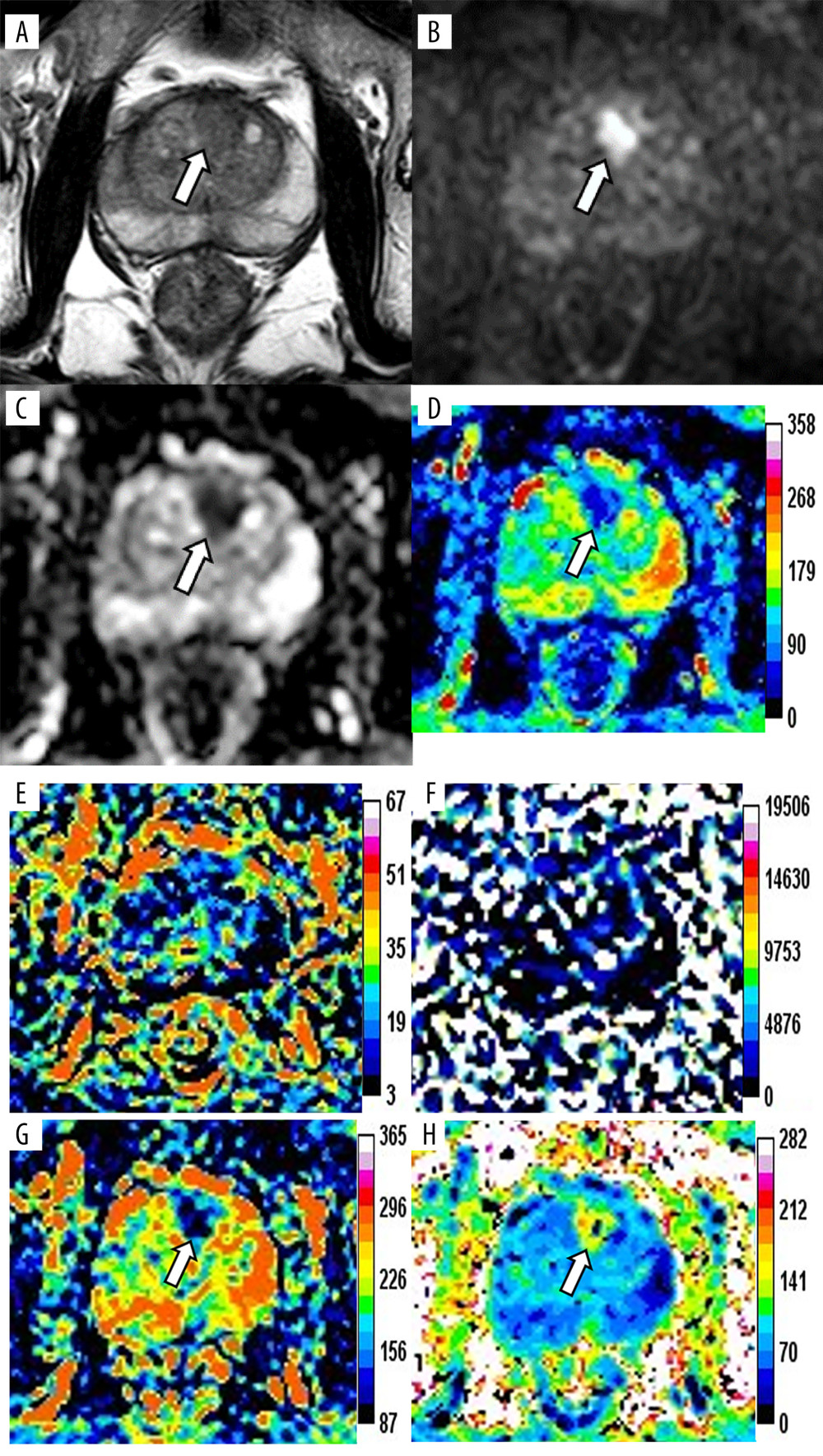
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance images of a 76-year-old patient with prostate cancer (PCa), total prostate-specific antigen (PSA) of 23.48 ng/mL, free/total PSA of 0.145, and PSA density of 0.34 ng/mL/cm3. The axis T2-weighted imaging (A) shows a low-signal area at the anterior of the transitional zone (white arrow). The lesion appears as a significantly high signal change on diffusion-weighted imaging (B, white arrow), whereas it appears as a low signal on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) (C, white arrow). The pseudo-color maps of D (D), Dapp (G), and Kapp (H) show the lesion clearly (white arrow). The image quality of f (E) and D* (F) are unsatisfactory. The parameter values of the lesion are 0.66×10−3 mm2/s (ADC), 0.64×10−3 mm2/s (D), 0.12 (f), 90.59×10−3 mm2/s (D*), 0.94×10−3 mm2/s (Dapp), and 1.19 (Kapp). The prediction probability (P) of the lesion being cancer can be calculated as follows:P=e(4.339+3.896×0.340-7.130×0.660)1+e(4.339+3.896×0.340-7.130×0.660)=72.2%. (Ingenia 3.0T,PHILIPS;PRIDE DWI Tool 1.5,PHILIPS;Image J 1.52a,NIH).


