Page Not Found
The page you are looking for was not found. Please use the search engine or the website menu.

Latest Articles
24 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variation of Medical Comorbidities in Oral Surgery Patients: A Retrospective Study at Jazan University
Fareedi Mukram Ali ![]() , Ghassan M. Al-Iryani
, Ghassan M. Al-Iryani ![]()
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943884
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943884
24 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variation of Medical Comorbidities in Oral Surgery Patients: A Retrospective Study at Jazan University
Fareedi Mukram Ali ![]() , Ghassan M. Al-Iryani
, Ghassan M. Al-Iryani ![]()
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943884
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943884
23 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Enhanced Surgical Outcomes of Popliteal Cyst Excision: A Retrospective Study Comparing Arthroscopic Debridement with and without Methylene Blue Injection
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.941102
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e941102
23 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Enhanced Surgical Outcomes of Popliteal Cyst Excision: A Retrospective Study Comparing Arthroscopic Debridement with and without Methylene Blue Injection
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.941102
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e941102
22 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Predicting Acute Cardiovascular Complications in COVID-19: Insights from a Specialized Cardiac Referral Department
Michał Machowski ![]() , Aisha Ou-Pokrzewińska
, Aisha Ou-Pokrzewińska
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942612
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942612
22 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Predicting Acute Cardiovascular Complications in COVID-19: Insights from a Specialized Cardiac Referral Department
Michał Machowski ![]() , Aisha Ou-Pokrzewińska
, Aisha Ou-Pokrzewińska
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942612
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942612
21 Apr 2024 : Meta-Analysis
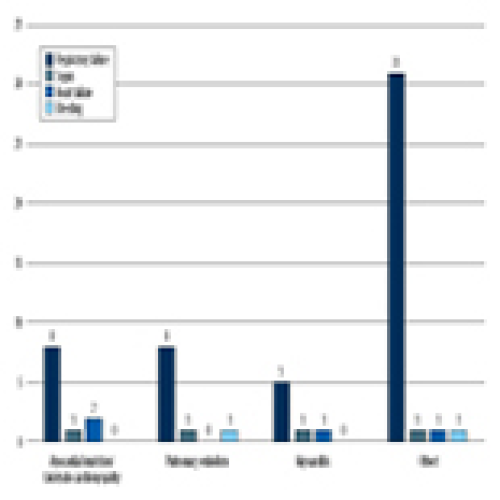
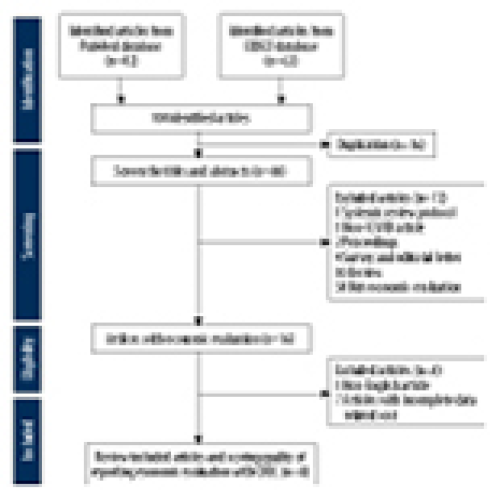
Economic Evaluation of COVID-19 Screening Tests and Surveillance Strategies in Low-Income, Middle-Income, and High-Income Countries: A Systematic Review
Abdul Khairul Rizki Purba ![]() , Alfian Nur Rosyid
, Alfian Nur Rosyid
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943863
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943863

21 Apr 2024 : Meta-Analysis
Economic Evaluation of COVID-19 Screening Tests and Surveillance Strategies in Low-Income, Middle-Income, and High-Income Countries: A Systematic Review
Abdul Khairul Rizki Purba ![]() , Alfian Nur Rosyid
, Alfian Nur Rosyid
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943863
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943863
20 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparison of Outcomes between Single-Level and Double-Level Corpectomy in Thoracolumbar Reconstruction: A Retrospective Study of 16 Patients Using Expandable Cages
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943797
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943797
20 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparison of Outcomes between Single-Level and Double-Level Corpectomy in Thoracolumbar Reconstruction: A Retrospective Study of 16 Patients Using Expandable Cages
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943797
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943797
19 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Role of Critical Shoulder Angle in Degenerative Type Rotator Cuff Tears: A Turkish Cohort Study
Mehmed Nuri Tütüncü, Yiğit Kültür
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943703
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943703
19 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Role of Critical Shoulder Angle in Degenerative Type Rotator Cuff Tears: A Turkish Cohort Study
Mehmed Nuri Tütüncü, Yiğit Kültür
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943703
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943703
18 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Effects of Thermal Insulation on Recovery and Comfort of Patients Undergoing Holmium Laser Lithotripsy
Xiaoling Chen, Libin He
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942836
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942836
18 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Effects of Thermal Insulation on Recovery and Comfort of Patients Undergoing Holmium Laser Lithotripsy
Xiaoling Chen, Libin He
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942836
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942836
17 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Muscular Function Recovery from General Anesthesia in 132 Patients Undergoing Surgery with Acceleromyography, Combined Acceleromyography, and Ultrasonography, and without Monitoring Muscular Function
Shiqian Huang, Yu Pan
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942780
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942780
17 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Muscular Function Recovery from General Anesthesia in 132 Patients Undergoing Surgery with Acceleromyography, Combined Acceleromyography, and Ultrasonography, and without Monitoring Muscular Function
Shiqian Huang, Yu Pan
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942780
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942780
16 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparative Analysis of Transoral Endoscopic Parathyroidectomy Vestibular Approach and Focused Open Surgery for Primary Hyperparathyroidism Treatment: A Single Center Experience
Mehmet Zafer Sabuncuoglu ![]() , Isa Sozen
, Isa Sozen
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944128
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e944128
16 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparative Analysis of Transoral Endoscopic Parathyroidectomy Vestibular Approach and Focused Open Surgery for Primary Hyperparathyroidism Treatment: A Single Center Experience
Mehmet Zafer Sabuncuoglu ![]() , Isa Sozen
, Isa Sozen
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.944128
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e944128
15 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Evaluation of the Interrater Reliability of Sonographic Measurements of Muscle Thickness of 38 Piriformis Muscles in 19 Patients with Piriformis Syndrome
Sibel Caglar, Ozden Ozyemisci-Taskiran
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943720
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943720
15 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Evaluation of the Interrater Reliability of Sonographic Measurements of Muscle Thickness of 38 Piriformis Muscles in 19 Patients with Piriformis Syndrome
Sibel Caglar, Ozden Ozyemisci-Taskiran
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943720
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943720
14 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Injury-Admission Time is an Independent Risk Factor for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Older Patients with Osteoporotic Hip Fracture
Xiuli Cui, Qingjun Liu
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943587
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943587
14 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Injury-Admission Time is an Independent Risk Factor for Deep Vein Thrombosis in Older Patients with Osteoporotic Hip Fracture
Xiuli Cui, Qingjun Liu
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943587
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943587
13 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Effect of Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Retinopathy of Prematurity in Preterm Newborns: A Comparative Analysis with Mechanical Ventilation and High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy
Daniela M. Cioboata, Aniko M. Manea
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943486
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943486
13 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Effect of Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure on Retinopathy of Prematurity in Preterm Newborns: A Comparative Analysis with Mechanical Ventilation and High-Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy
Daniela M. Cioboata, Aniko M. Manea
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943486
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943486
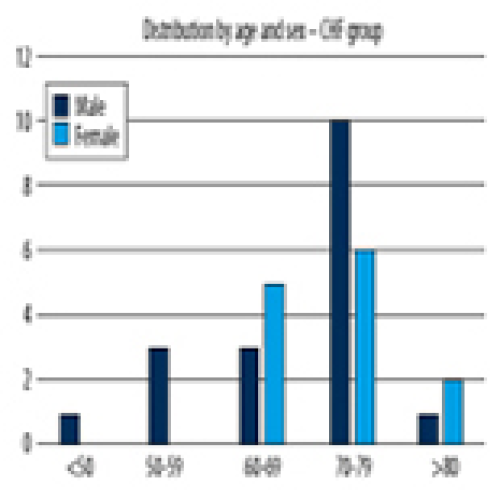
12 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Quality of Life of Chronic Heart Failure Patients During and After COVID-19: Observational Study Using EuroQoL-Visual Analogue Scales
Emoke Ilona Sukosd, Nilima Rajpal Kundnani ![]()
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943301
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943301
12 Apr 2024 : Clinical Research
Quality of Life of Chronic Heart Failure Patients During and After COVID-19: Observational Study Using EuroQoL-Visual Analogue Scales
Emoke Ilona Sukosd, Nilima Rajpal Kundnani ![]()
DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943301
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e943301
Editorial
01 April 2024 : Editorial
Editorial: Forty Years of Waiting for Prevention and Cure of HIV Infection – Ongoing Challenges and Hopes for Vaccine Development and Overcoming Antiretroviral Drug ResistanceDOI: 10.12659/MSM.944600
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e944600
In Press
08 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Evaluation of Foot Structure in Preschool Children Based on Body MassMed Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943765
15 Apr 2024 : Laboratory Research
The Role of Copper-Induced M2 Macrophage Polarization in Protecting Cartilage Matrix in OsteoarthritisMed Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943738
07 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Knowledge of and Attitudes Toward Clinical Trials: A Questionnaire-Based Study of 179 Male Third- and Fourt...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943468
08 Mar 2024 : Animal Research
Modification of Experimental Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) in Rat Pups by Single Exposure to Hyp...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943443
Most Viewed Current Articles
17 Jan 2024 : Review article
Vaccination Guidelines for Pregnant Women: Addressing COVID-19 and the Omicron VariantDOI :10.12659/MSM.942799
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942799
14 Dec 2022 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variability of Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin E in Patients with Elevated Tryptase LevelsDOI :10.12659/MSM.937990
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e937990
16 May 2023 : Clinical Research
Electrophysiological Testing for an Auditory Processing Disorder and Reading Performance in 54 School Stude...DOI :10.12659/MSM.940387
Med Sci Monit 2023; 29:e940387
01 Jan 2022 : Editorial
Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Pa...DOI :10.12659/MSM.935952
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935952


