05 September 2021: Animal Study
Live Combined and Alleviate Liver Inflammation, Improve Intestinal Barrier Function, and Modulate Gut Microbiota in Mice with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Jie Jiang1BCDE, Jie Xiong1ACEFG*, Jianbo Ni2CDE, Congying Chen2CD, Kezhou Wang3CDOI: 10.12659/MSM.931143
Med Sci Monit 2021; 27:e931143
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a chronic, progressive liver disease with an increasing incidence rate. This study investigated the protective effects of live combined Bacillus subtilis and Enterococcus faecium (LCBE) on NAFLD, and its possible mechanisms.
MATERIAL AND METHODS: Five-week-old C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into 3 groups: chow, HFD, and HFD+LCBE groups. The levels of serum biochemical markers, glucose tolerance, insulin, the inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, LPS, and histological staining were measured using commercial kits. qPCR was used to examine the mRNA expression levels of inflammatory cytokines in the liver. Western blotting was used to determine the protein levels of TLR4, NF-κB p65, PPAR-α, and CPT-1 in the liver, and occludin and Claudin1 in the intestine. The intestinal flora of the mice was analyzed by high-throughput sequencing of the V3-V4 region of 16S rDNA.
RESULTS: LCBE significantly lowered the body weight, liver/body weight ratio, and serum glucose level, and increased the serum insulin level in NAFLD mice. In addition, LCBE treatment improved the liver function and lipid profile, decreased the levels of LPS and inflammatory cytokines, and downregulated the expression of TLR4 and NF-κB p65. Moreover, LCBE enhanced the intestinal barrier function by increasing the expression of occludin and Claudin1. Furthermore, LCBE modulated the composition of the gut microbiota by reducing the Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes ratio, and the proportion of inflammation-related and LPS-producing bacteria, thus re-arranging the structure of the gut microbiota.
CONCLUSIONS: LCBE protects against NAFLD by alleviating inflammation, restoring the intestinal barrier, and modulating gut microbiota composition.
Keywords: Bacillus subtilis, Enterococcus faecium, Liver Diseases, Animals, Anti-Inflammatory Agents, Non-Steroidal, Enterococcus faecalis, Glucose Tolerance Test, Hepatitis, Insulin Resistance, Intestinal Mucosa, Mice, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, Weight Gain
Background
Owing to the significant increase in obesity rates worldwide, the incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a metabolic syndrome, has also increased, and it is not restricted to developed countries. The disease spectrum of NAFLD is wide, ranging from simple steatosis to more serious forms, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatic cellular carcinoma [1]. This disorder affects the health of both adults and children, leading to a worldwide disease burden [2,3]. Despite the in-depth research on NAFLD, its pathogenesis remains poorly understood. A series of studies has focused on the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of NAFLD [4]. Excess LPS flux to the liver from the gut triggers an inflammatory response in the liver [5]. Additionally, obesity induces the recruitment of inflammatory cells, such as macrophages, and results in an increase in the release of inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α and IL-1β, aggravating the pathogenesis of NAFLD [6]. It is widely accepted that the “multiple hits” hypothesis is involved in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. Recent studies have provided evidence that gut microbiota, one of the key factors in the “multiple hits,” play an important role in the progression of NAFLD [7–10].
The number of human intestinal microbial cells, ranging from 100 trillion to 1000 trillion, is approximately 10 times the number of human cells in the body [11]. An imbalance of the gut microbiota is related to chronic diseases, including NAFLD.
Live combined
Material and Methods
ANIMALS AND EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN:
All experimental procedures were conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the National Research Council Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were approved by the Committee on Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the Medical College of Tongji University, China (TJHBLAC-2020-72).
Male C57BL/6J mice (5 weeks old) were procured from Shanghai Silaike Experimental Animal Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). All the mice were acclimatized in a controlled environment (temperature 20–24°C; relative humidity 60–70%, 12-h daylight cycle) with free access to food and water. After 1 week of acclimation, the mice were randomly allocated into 3 groups: (1) chow group (the mice received a chow diet, n=5); (2) HFD group (the mice received an HFD, n=5); and (3) LCBE group (the mice received an HFD and LCBE by gavage once daily, n=6). The chow group was fed a chow diet, and the HFD and LCBE groups were fed with an HFD providing 60% kcal fat from TROPHIC Animal Feed High-Tech Co. Ltd. (Jiangsu, China), for 16 weeks. The LCBE group mice received 0.5 mL LCBE containing 1.4×109 CFU of
BIOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS:
Serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (Cho), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) were measured using commercial kits (Jiancheng Biomedical Company, Nanjing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The serum levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-β, and IL-6, were detected using ELISA kits (Jingmei, Jiangsu, China). After a 16-h fast, the mice were administered glucose (2.0 g/kg, intraperitoneally). Blood was obtained from the tail vein at 0, 15, 30, 60, and 120 min to measure blood glucose levels using a glucometer (ACCU-CHEK, Roche Diabetes, Germany). ELISA was performed using commercial kits to measure the serum insulin levels (Cusabio, Wuhan, China) and serum LPS levels (Bioendo Technology Co., Xiamen, China). The method for representing insulin sensitivity was based on the homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), which was calculated as follows:
HISTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:
Livers and intestines were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 h at 4°C, embedded in paraffin, and sliced into 4-μm slices for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. To detect lipid deposition in the liver, liver samples were frozen, cut into 8-μm-thick sections, and stained with Oil Red O. The sections were visualized and imaged using a light microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan).
RNA ISOLATION AND QUANTITATIVE REAL-TIME PCR (QPCR):
Total RNA was isolated from liver tissues using TRIzol reagent (Takara, Dalian, China) and reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a cDNA synthesis kit (RR036A, Takara, Dalian, China).
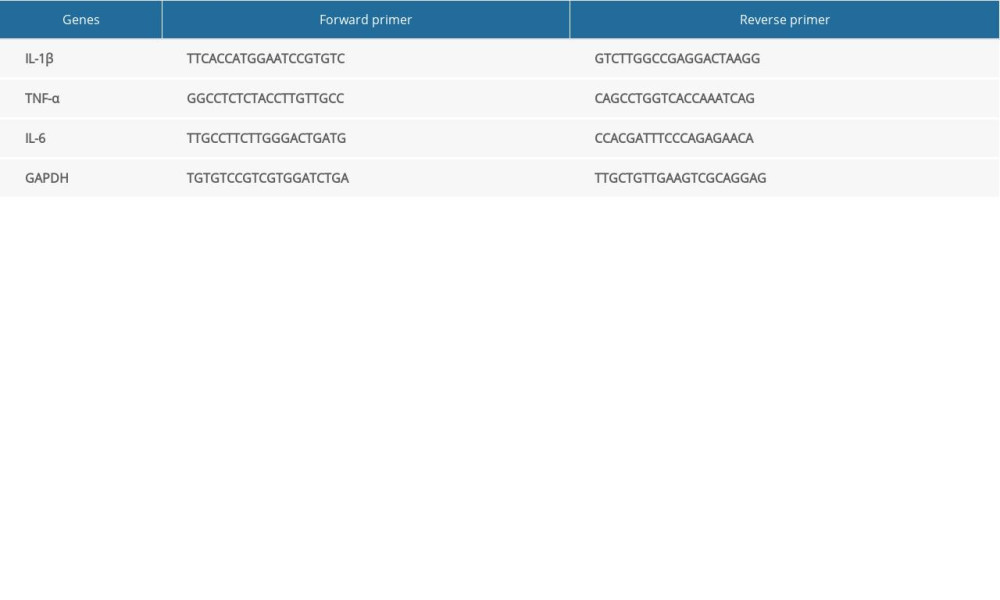
Specific gene expression was detected by qPCR using SYBR Green (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) with an Applied Biosystems QuantStudio 5 instrument. Relative gene expression was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method. The primers used in this study are shown in Table 1.
WESTERN BLOTTING:
Protein extracts were prepared using a protein lysis kit (Beyotime, China) with a protease inhibitor (Beyotime), and protein lysates were separated using 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Next, the proteins in the gel were transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes (Merck Millipore). The membranes were washed and blocked with 5% BSA in Tris-buffered saline and Tween-20 (TBST) for 1 h at room temperature. The membranes were then incubated with primary antibodies, including anti-NF-κB (1: 2000, Proteintech, 66535-1-lg), anti-TLR4 (3.5 μg/mL, Abcam, ab13867), anti-CPT-1 (1: 1000, Proteintech,15184-1-AP), anti-PPAR-α (1 μg/mL, Abcam, ab126285), anti-Claudin1 (1: 5000, Abcam, ab180158), anti-occludin (1: 1000, Abcam, ab167161), and anti-GAPDH (1: 25000, Proteintech, 60004-1-lg) for 16 h at 4°C. After washing with TBST, the membranes were incubated with IgG conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (HRP; Thermo Fisher, USA) for 1 h at room temperature. Finally, enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL; Beyotime) was employed to detect protein bands using the ChemiDoc XRS system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, CA, United States). Densitometry analysis of each band was conducted using ImageJ software.
BACTERIAL DNA EXTRACTION AND 16S RDNA BIOINFORMATICS ANALYSIS:
Total DNA from colonic contents was extracted using the TIANamp Stool DNA Kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). After confirming the DNA integrity, the V3–V4 region of the bacterial 16S rDNA was amplified according to the following cycling conditions: initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 min, and 30 cycles of 94°C for 20 s, 55°C for 20 s, and 72°C for 30 s. The 16S rDNA PCR primers used were as follows: 341F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). After extraction based on quantitative analysis, and purification, the amplicons were merged at a ratio of 1: 1. A library was constructed using an Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered with 97% sequence identity based on the 16S raw data sequence, which was analyzed using QIIME (Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology).
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS:
All data are expressed as means±standard deviations (SD) for each group, and data analysis was performed using SPSS software version 20.0. The differences among groups were determined by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and
Results
LCBE PREVENTS ABNORMAL GAIN OF BODY WEIGHT AND LIVER INDEX AND IMPROVES GLUCOSE TOLERANCE AND INSULIN RESISTANCE:
To examine the effects of LCBE on NAFLD in mice, we determined their body weights, and found that the body weight in the HFD group was higher than that in the chow group for 16 weeks (Figure 1A). LCBE treatment significantly prevented abnormal body weight gain in HFD-fed mice (Figure 1A). Furthermore, the HFD increased the liver index compared with that in the chow group, and LCBE intervention reversed this (Figure 1B). Additionally, we assessed the glucose levels and insulin sensitivity, and the results showed that HFD-fed mice had higher blood glucose, serum insulin, and HOMA-IR levels than mice in the chow group (Figure 1C–1E). LCBE administration improved the blood glucose, serum insulin, and HOMA-IR levels, indicating that LCBE improved glucose tolerance and IR in the HFD-fed mice.
LCBE ALLEVIATE HEPATIC STEATOSIS:
We assessed the serum lipid parameters in all the groups and found that HFD remarkably elevated the levels of serum TG, Cho, and LDL, and decreased the level of serum HDL (Figure 2A–2D). LCBE intervention markedly decreased the serum TG, Cho, and LDL levels, and upregulated the serum HDL levels compared with those in the HFD group (Figure 2A–2D). In addition, LCBE significantly reduced the high serum levels of ALT and AST induced by the HFD (Figure 2E, 2F). Since LCBE affected serum lipid homeostasis and liver function in NAFLD mice, we detected the expression of PPAR-α and CPT-1, and conducted histological analyses of the liver, including H&E and Oil Red O staining, to determine the role of LCBE in hepatic steatosis. We found that LCBE treatment elevated the protein expression levels of PPAR-α and CPT-1 in the livers of HFD-fed mice (Figure 2G, 2H). As shown in Figure 2I, there were more lipid droplets in the livers of NAFLD mice than in the chow group, whereas LCBE treatment distinctly alleviated abnormal lipid accumulation in the liver.
LCBE REDUCES INFLAMMATORY RESPONSE:
Based on the important role of the inflammatory response in the development and progression of NAFLD, the expression levels of genes associated with inflammation were determined. The expression levels of serum IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were higher in the HFD group than in the chow group (Figure 3A–3C). Interestingly, treatment with LCBE remarkably reduced the IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels (Figure 3A–3C). We measured the expression of inflammatory cytokines in the liver. Consistent with the above results, the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α was significantly higher in the HFD group than in the chow group, but the expression of these inflammatory cytokines was markedly decreased by LCBE (Figure 3D–3F). Furthermore, we performed western blotting to determine the expression of genes related to inflammatory signaling pathways, such as those of TLR4 and NF-κB p65. Compared with the control group, the HFD group showed higher expression of TLR4 and NF-κB, whereas LCBE intervention prevented the increase in TLR4 and NF-κB p65 levels in the liver (Figure 3G, 3H).
LCBE REDUCES SERUM LPS LEVELS AND IMPROVES INTESTINAL BARRIER INTEGRITY:
Intestinal barrier integrity not only affects systemic inflammation but is also involved in the development of NAFLD. H&E staining of the intestine revealed that the intestinal mucosa villi in chow group were slim, neatly arranged, and integral. However, the intestinal mucosa villi in the HFD group showed edema and the villus height was decreased; this was repaired to a certain degree by LCBE intervention (Figure 4A). Moreover, LPS, translocating into the blood recycle from a leaky gut, reflects the integrity of the intestinal barrier. We found that the expression of serum LPS was higher in the HFD group than in the chow group, and LCBE intervention decreased LPS expression (Figure 4B). Epithelial tight junction molecules play a critical role in intestinal barrier integrity. As expected, the protein levels of occludin and Claudin1 were lower in the HFD group than in the chow group (Figure 4C, 4D). In contrast, LCBE treatment reversed the downregulation of these proteins in NAFLD mice (Figure 4C, 4D).
LCBE REGULATES INTESTINAL FLORA COMPOSITION OF GUT MICROBIOTA:
The V3–V4 region of 16S rDNA in mice fecal samples was used to evaluate the effects of LCBE on the microbiota. The Shannon dilution curve tended to be smooth for all the samples, indicating that the sequencing depth was sufficient to reveal the biodiversity in the samples (Figure 5A). Next, we conducted PCoA and NMDS analyses to investigate the effects of LCBE on the gut microbiota structure. The PCoA and NMDS of the unweighted UniFrac distance showed a remarkable separation among the compositions of gut microbiota in the chow, HFD, and LCBE groups (Figure 5B, 5C). In addition, the microbes in the gut of the mice could be classified into 15 phyla, and Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes were the dominant bacterial phyla in all the groups. As shown in Figure 5D, the microbial composition in the HFD group was remarkably different from that in the chow group. At the phylum level, the HFD increased the abundance of Firmicutes and decreased that of Bacteroidetes compared with that in the chow group (Figure 5F, 5G). Therefore, the HFD significantly increased the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes (F/B ratio). LCBE treatment reversed the F/B ratio by downregulating the abundance of Firmicutes and upregulating the abundance of Bacteroidetes (Figure 5E). In addition, the relative abundance of Verrucomicrobia, Actinobacteria, and Patescibacteria changed at the phylum level (Figure 5H–5J). Furthermore, the LDA effect size (LEfSe) method was used to determine the different bacterial taxa. The results from LEfSe analysis demonstrated that some genera (Figure 6A), such as Akkermansia, Ruminococcus_UCG-014, Family_XIII_AD3011_group, Oscillibacter, Acetatifactor, Coriobacterium_UCG-002, Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group, Anaerovorax, Negativibacillus, Lachnoclostridium, Angelakisella, Ruminococcus, Harryflintia, and Escherichia-Shigella, were notably different. Compared with that in the chow group, the HFD promoted a remarkable increase in the relative abundance of Akkermansia, Lachnoclostridium, Oscillibacter, Family_XIII_AD3011_group, Anaerovorax, Acetatifactor, Coriobacterium_UCG-002, Negativibacillus, Angelakisella, Ruminococcus, Harryflintia, and Escherichia-Shigella (Figure 6B–6M), while decreasing the relative abundance of Ruminococcus_UCG-014 and Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group (Figure 6N, 6O). The administration of LCBE dramatically elevated the relative abundance of Akkermansia, Ruminococcus_UCG-014, and Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group, and reduced that of Lachnoclostridium, Oscillibacter, Family_XIII_AD3011_group, Anaerovorax, Acetatifactor, Coriobacterium_UCG-002, Negativibacillus, Angelakisella, Ruminococcus, Harryflintia, and Escherichia-Shigella. These results indicated that LCBE modulated gut microbiota dysbiosis by promoting beneficial bacterial proliferation and inhibiting harmful flora expansion.
Discussion
NAFLD is a worldwide health issue that is associated with obesity. Although lifestyle modifications and exercise have been suggested for NAFLD treatment, both are difficult to execute. In addition, there is a lack of effective drugs targeting NAFLD. Therefore, it is of great importance to identify drugs that can treat NAFLD. Previous studies have indicated that probiotics significantly prevent HFD-induced NAFLD in mice [21,22]. Hence, LCBE is believed to alleviate NAFLD. In this study, we found that treatment with LCBE protected NAFLD mice fed with an HFD by partially enhancing insulin sensitivity, alleviating the inflammatory response, improving the function of the intestinal barrier, and regulating the composition of gut microbiota.
Abnormal blood glucose levels and the accumulation of excessive lipids in the liver are common in NAFLD mice. The results of our research showed that the HFD increased the body weight and liver index, and caused dyslipidemia and glucose intolerance, which were reversed by the LCBE intervention. Triglyceride accumulation in the liver is affected by many factors, including fatty acid uptake, synthesis, oxidation, and transporters [23]. Insulin resistance is the “first hit” in NAFLD [24]. Insulin resistance decreases lipid oxidation in the liver, and the PPAR-α and CPT-1 genes have been identified as the key fatty acid oxidation genes that can alleviate NAFLD by promoting lipid oxidation [25]. The results of this study showed that the HFD enhanced insulin resistance and HOMA-IR, and this was prevented by LCBE. In addition, we found that LCBE treatment significantly upregulated the expression levels of hepatic PPAR-α and CPT-1, indicating that fatty acid β-oxidation plays a critical role in alleviating dyslipidemia and hepatic steatosis upon the administration of LCBE. Therefore, an increase in insulin sensitivity plays an important role in alleviating hepatic steatosis upon LCBE intervention.
Since the inflammatory response participates in the development of NAFLD, we assessed the effect of LCBE on inflammation in NAFLD mice. In addition, a previous study verified that
Previous studies have shown that the intestinal barrier plays a key role in NAFLD induced by a high-fat or high-fructose diet [29–31]. The physical intestinal barrier is an important component of the intestinal barrier [32]. Recently, the physical intestinal barrier was widely studied in relation to HFD-obesity gut permeability, which enhances the translocation of LPS and harmful bacteria from the gut to the liver via blood circulation [28,33]. Since LPS reflects the leaky gut and LCBE can reduce the serum LPS levels, the intestinal integrity in NAFLD mice was affected by LCBE treatment. LCBE promoted the upregulation of tight junction proteins such as occludin and Claudin1. In addition, unlike the chow group, the HFD group exhibited damaged intestinal structure integrity, which was restored by LCBE. These data indicated that LCBE maintained the strength of the intestinal physical barrier in NAFLD mice.
An increasing number of studies are showing that gut microbiota play a vital role in the development of NAFLD by harvesting energy and modulating energy metabolism.
Our study has one limitation. Additional methods, such as FITC dextran tests, should be used to determine the intestinal permeability.
Conclusions
In summary, our study showed that LCBE administration significantly alleviated HFD-induced NAFLD. Mechanistically, LCBE modulated gut microbiota dysbiosis by increasing species richness and diversity. Moreover, LCBE alleviated liver inflammation, reduced serum LPS levels, and improved the intestinal barrier function. These data suggest that LCBE may be a potential candidate for the treatment of NAFLD.
Figures
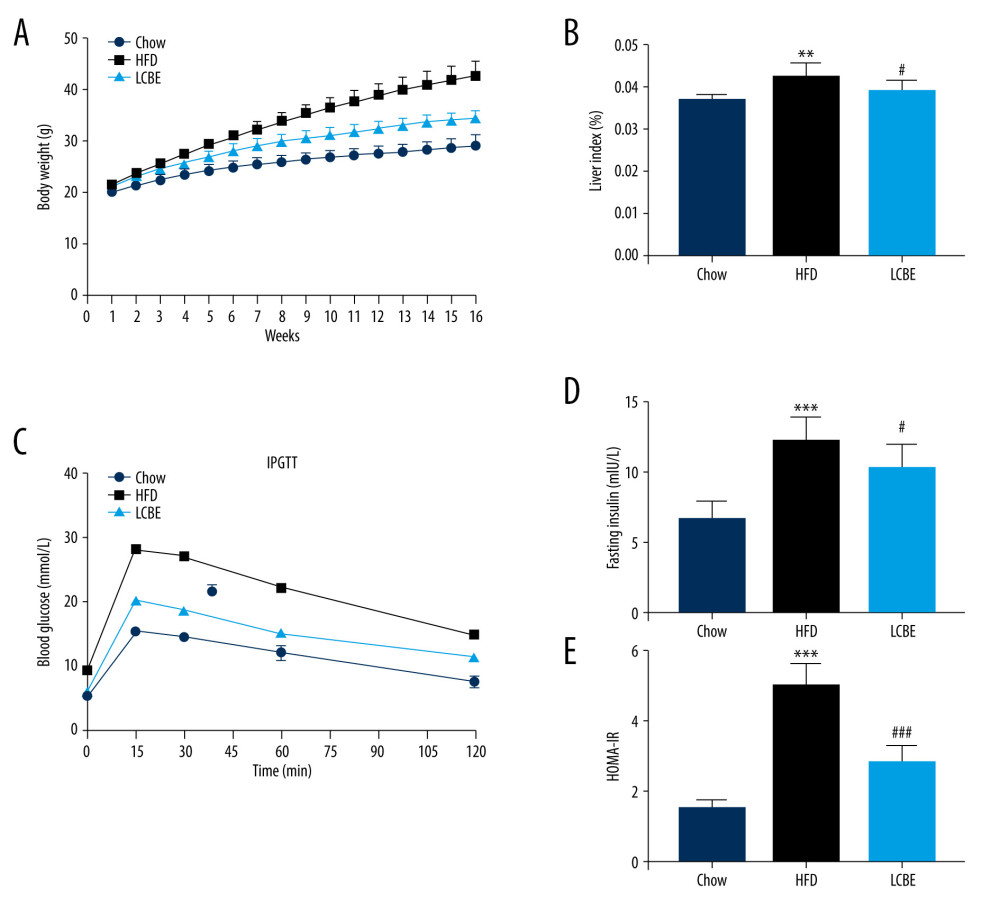 Figure 1. LCBE prevents abnormal weight, liver weight, and liver index levels, and improves glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). (A) Body weight; (B) liver index; and (C) blood glucose concentration in the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT); (D) levels of serum insulin; and (E) determination of HOMA-IR. The data are expressed as means±SD. # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs Chow, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 1. LCBE prevents abnormal weight, liver weight, and liver index levels, and improves glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). (A) Body weight; (B) liver index; and (C) blood glucose concentration in the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT); (D) levels of serum insulin; and (E) determination of HOMA-IR. The data are expressed as means±SD. # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs Chow, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs HFD. 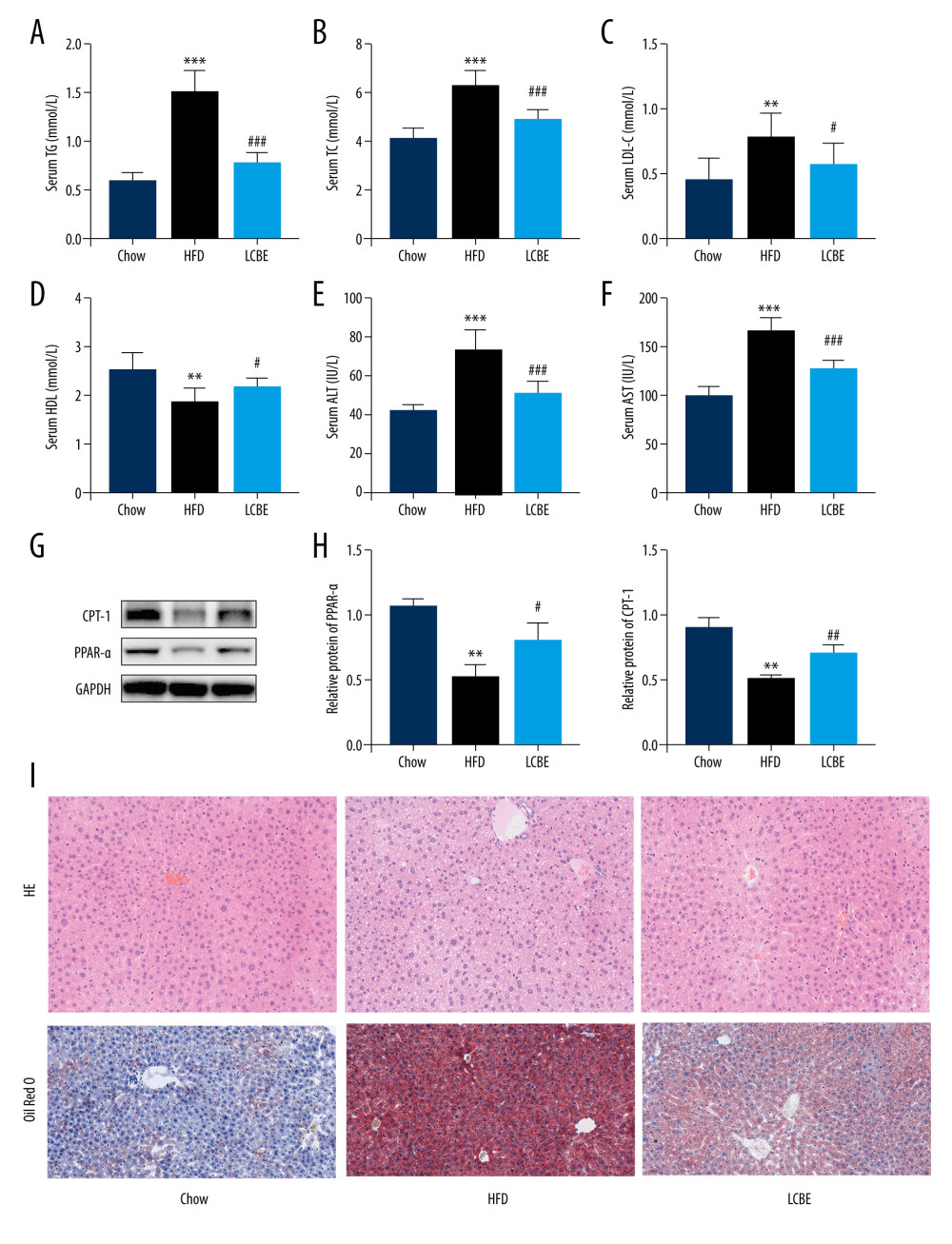 Figure 2. Effect of LCBE on serum lipid metabolism, ALT, and AST levels in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Serum triglyceride; (B) serum total cholesterol; (C) serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; (D) serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; (E) activity of serum ALT; (F) activity of serum AST; (G) histopathology images of liver tissues ((I) H&E, 200× magnification; Oil Red O, 200× magnification); and (H) protein expression levels of PPAR-α and CPT-1 in the liver. GAPDH was used in the loading chow. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 2. Effect of LCBE on serum lipid metabolism, ALT, and AST levels in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Serum triglyceride; (B) serum total cholesterol; (C) serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; (D) serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; (E) activity of serum ALT; (F) activity of serum AST; (G) histopathology images of liver tissues ((I) H&E, 200× magnification; Oil Red O, 200× magnification); and (H) protein expression levels of PPAR-α and CPT-1 in the liver. GAPDH was used in the loading chow. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. 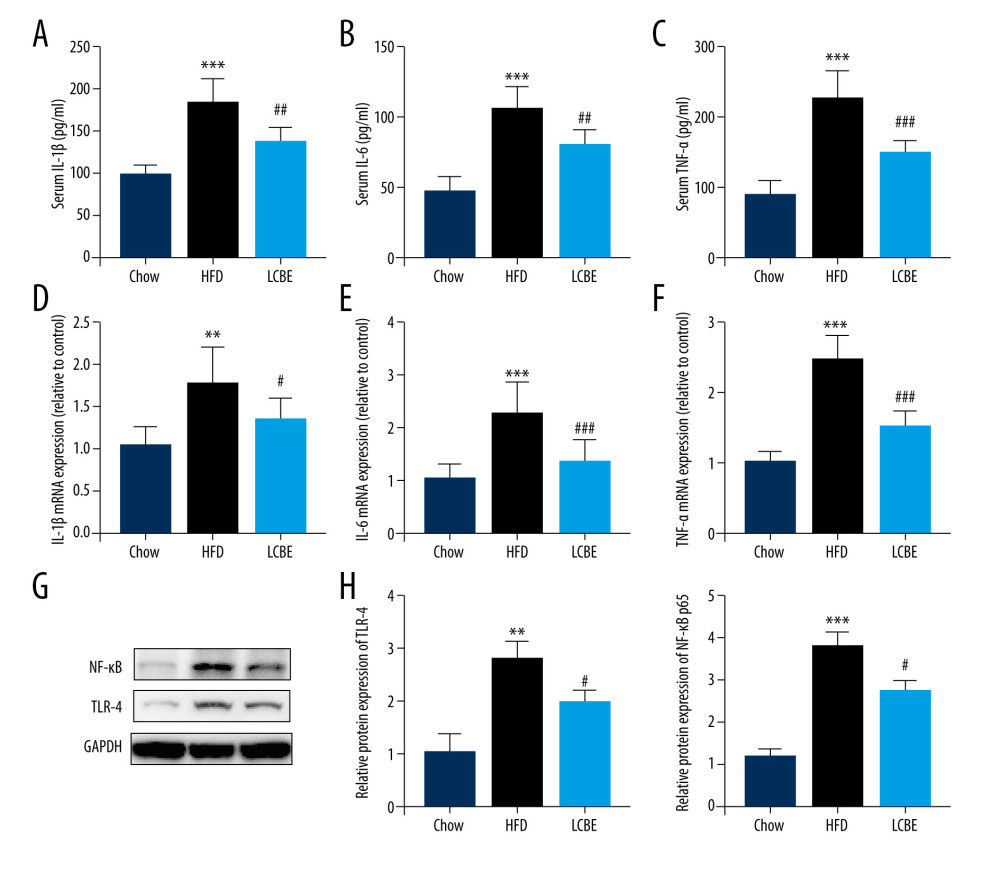 Figure 3. LCBE mitigates systemic inflammation in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). The levels of (A, D) interleukin 1β (IL-1β), (B, E) interleukin 6 (IL-6), and (C, F) tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in the serum and liver. (G–H) Protein expression levels of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in the liver. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 3. LCBE mitigates systemic inflammation in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). The levels of (A, D) interleukin 1β (IL-1β), (B, E) interleukin 6 (IL-6), and (C, F) tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in the serum and liver. (G–H) Protein expression levels of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in the liver. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. 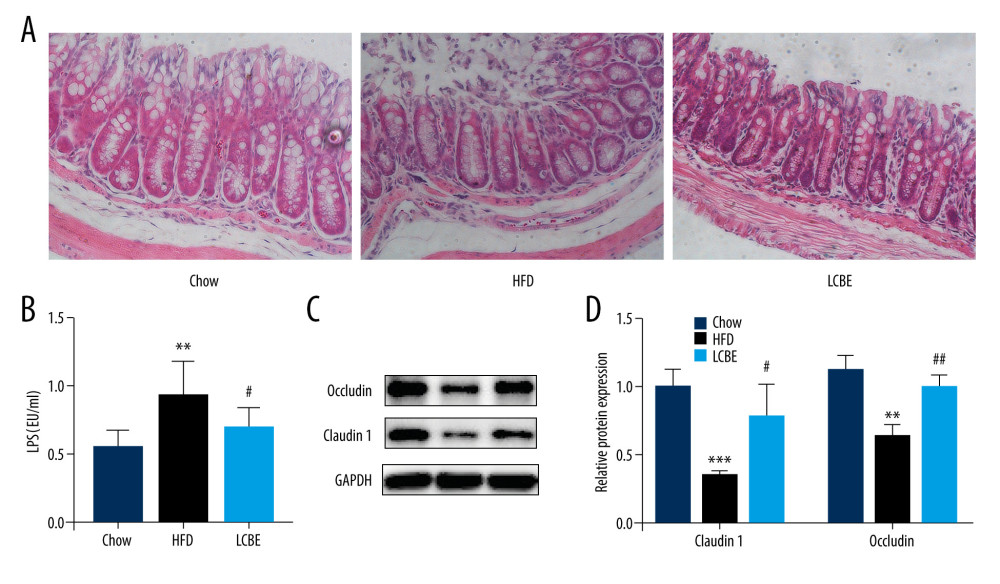 Figure 4. LCBE consolidates the intestinal barrier in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Histopathology images of intestine tissues (H&E, 200× magnification). (B) LPS levels in the serum. (C, D) Protein expression levels of occludin and Claudin1 in the intestine. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 4. LCBE consolidates the intestinal barrier in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Histopathology images of intestine tissues (H&E, 200× magnification). (B) LPS levels in the serum. (C, D) Protein expression levels of occludin and Claudin1 in the intestine. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. 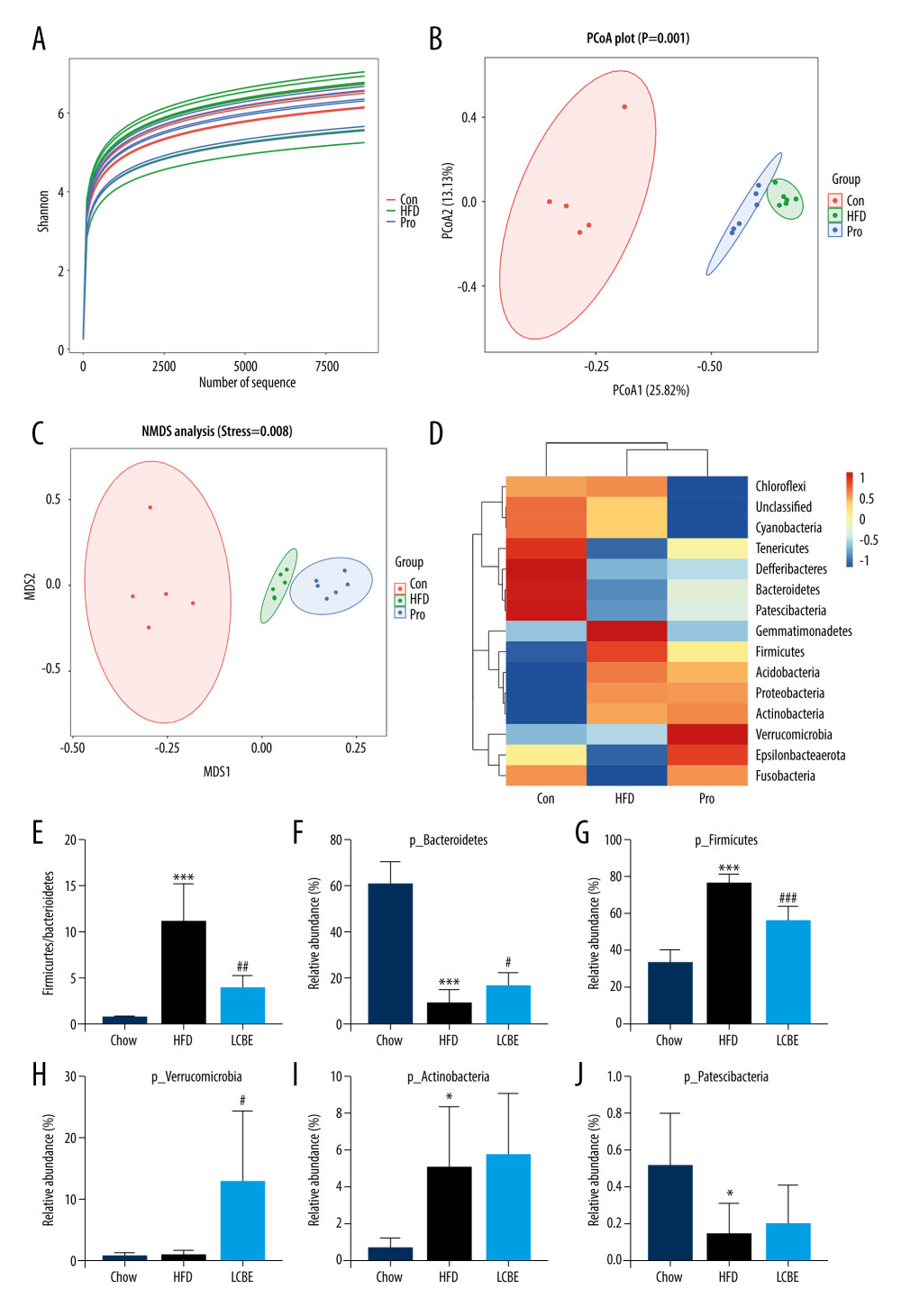 Figure 5. LCBE modulates the gut microbiota community in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Shannon curve of each sample. (B) Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of microbial communities based on the unweighted Unifrac cluster for each sample at the phylum level. (C) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of microbial communities based on the unweighted Unifrac cluster for each sample at the phylum level. (D) Relative abundance analysis of microbiota at the phylum level between groups. (E–J) Ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes and relative abundance of bacteria among groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 5. LCBE modulates the gut microbiota community in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Shannon curve of each sample. (B) Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of microbial communities based on the unweighted Unifrac cluster for each sample at the phylum level. (C) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of microbial communities based on the unweighted Unifrac cluster for each sample at the phylum level. (D) Relative abundance analysis of microbiota at the phylum level between groups. (E–J) Ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes and relative abundance of bacteria among groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. 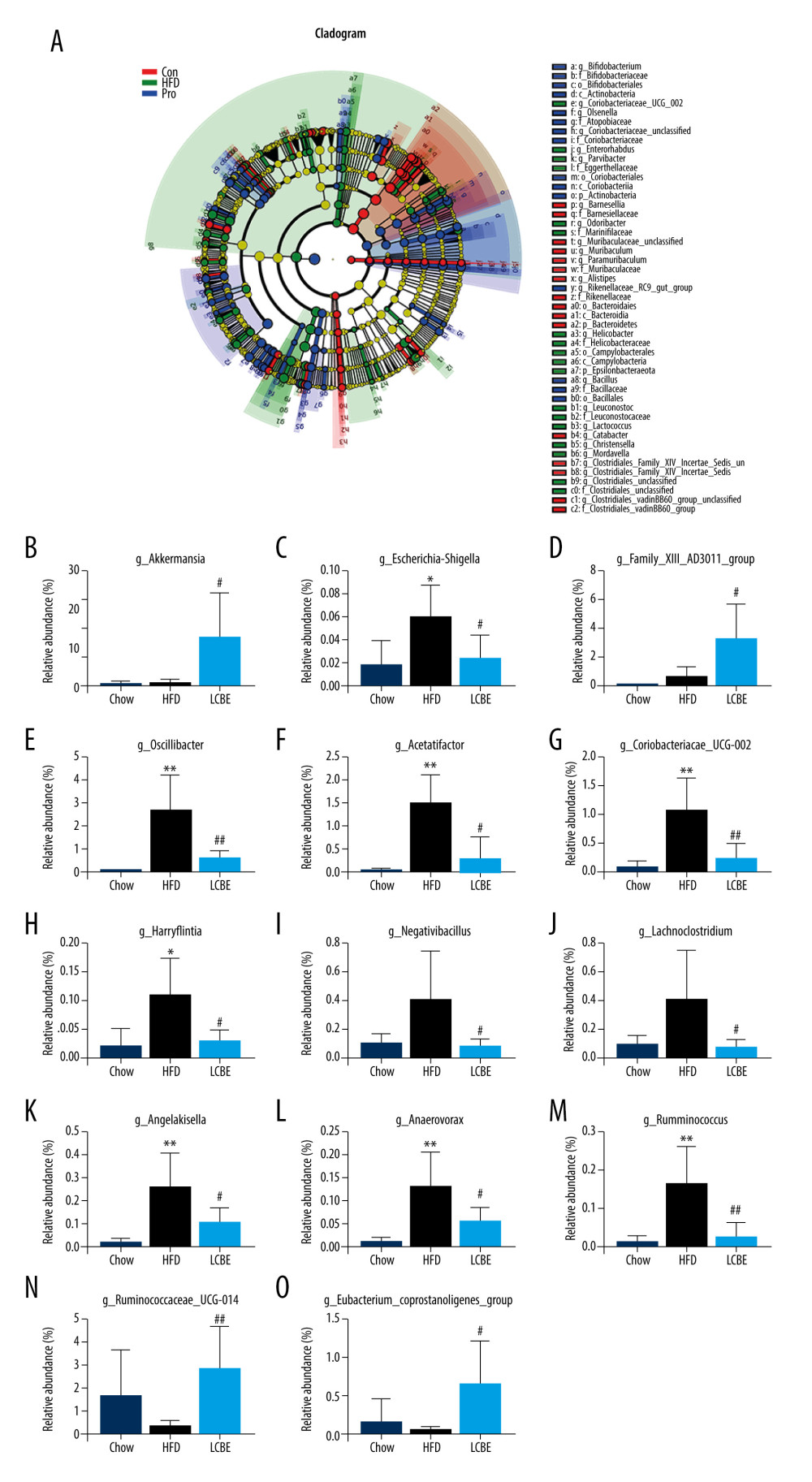 Figure 6. LCBE amends the gut microbiota at the genus level in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Taxonomic cladogram depicting enriched taxa that are differentially abundant in all groups with a LDA score >3.0. (B–O) Relative abundance of different bacteria in all groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 6. LCBE amends the gut microbiota at the genus level in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Taxonomic cladogram depicting enriched taxa that are differentially abundant in all groups with a LDA score >3.0. (B–O) Relative abundance of different bacteria in all groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. References
1. Karlas T, Wiegand J, Berg T, Gastrointestinal complications of obesity: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its sequelae: Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2013; 27(2); 195-208
2. Fan J-G, Farrell GC, Epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China: J Hepatol, 2009; 50(1); 204-10
3. Wang F-S, Fan J-G, Zhang Z, The global burden of liver disease: The major impact of China: Hepatology (Baltimore, Md), 2014; 60(6); 2099-108
4. Byrne CD, Fatty liver: Role of inflammation and fatty acid nutrition: Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids, 2010; 82(4–6); 265-71
5. Carpino G, Del Ben M, Pastori D, Increased liver localization of lipopolysaccharides in human and experimental NAFLD: Hepatology (Baltimore, Md), 2020; 72(2); 470-85
6. Oh DY, Morinaga H, Talukdar S, Increased macrophage migration into adipose tissue in obese mice: Diabetes, 2012; 61(2); 346-54
7. Lang S, Demir M, Martin A, Intestinal virome signature associated with severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Gastroenterology, 2020; 159(5); 1839-52
8. Craven L, Rahman A, Nair Parvathy S, Allogenic fecal microbiota transplantation in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease improves abnormal small intestinal permeability: A randomized control trial: Am J Gastroenterol, 2020; 115(7); 1055-65
9. Albillos A, de Gottardi A, Rescigno M, The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Pathophysiological basis for therapy: J Hepatol, 2020; 72(3); 558-77
10. Aron-Wisnewsky J, Vigliotti C, Witjes J, Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders: Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020; 17(5); 279-97
11. Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine: Science (New York, NY), 2005; 307(5717); 1915-20
12. Le Roy T, Llopis M, Lepage P, Intestinal microbiota determines development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice: Gut, 2013; 62(12); 1787-94
13. Chevalier C, Stojanović O, Colin DJ, Gut microbiota orchestrates energy homeostasis during cold: Cell, 2015; 163(6); 1360-74
14. Compare D, Coccoli P, Rocco A, Gut–liver axis: The impact of gut microbiota on non alcoholic fatty liver disease: Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2012; 22(6); 471-76
15. Paolella G, Mandato C, Pierri L, Gut-liver axis and probiotics: Their role in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: World J Gastroenterol, 2014; 20(42); 15518-31
16. Littman DR, Pamer EG, Role of the commensal microbiota in normal and pathogenic host immune responses: Cell Host Microbe, 2011; 10(4); 311-23
17. Miele L, Marrone G, Lauritano C, Gut-liver axis and microbiota in NAFLD: Insight pathophysiology for novel therapeutic target: Curr Pharm Des, 2013; 19(29); 5314-24
18. Zhao Z, Chen L, Zhao Y, Lactobacillus plantarum NA136 ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota, improving intestinal barrier integrity, and attenuating inflammation: Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2020; 104(12); 5273-82
19. Xue L, He J, Gao N, Probiotics may delay the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by restoring the gut microbiota structure and improving intestinal endotoxemia: Sci Rep, 2017; 7; 45176
20. Guo L, Meng M, Wei Y, Protective effects of live combined and in polymicrobial sepsis through modulating activation and transformation of macrophages and mast cells: Front Pharmacol, 2018; 9; 1506
21. Khan A, Ding Z, Ishaq M, Understanding the effects of gut microbiota dysbiosis on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the possible probiotics role: Recent updates: Int J Biol Sci, 2021; 17(3); 818-33
22. Vitetta L, Henson JD, Probiotics and synbiotics targeting the intestinal microbiome attenuate non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2020; 9(4); 526-29
23. Masarone M, Rosato V, Dallio M, Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018; 2018; 9547613
24. Zhang S, Guo F, Yu M, Reduced Nogo expression inhibits diet-induced metabolic disorders by regulating ChREBP and insulin activity: J Hepatol, 2020; 73(6); 1482-95
25. Yang X, Fu Y, Hu F, PIK3R3 regulates PPARα expression to stimulate fatty acid β-oxidation and decrease hepatosteatosis: Exp Mol Med, 2018; 50(1); e431
26. Fujita M, Kuraji R, Ito H: J Periodontol, 2018; 89(9); 1101-11
27. Zhao G-N, Zhang P, Gong J, Tmbim1 is a multivesicular body regulator that protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice and monkeys by targeting the lysosomal degradation of Tlr4: Nat Med, 2017; 23(6); 742-52
28. Fei N, Bruneau A, Zhang X, Endotoxin producers overgrowing in human gut microbiota as the causative agents for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: mBio, 2020; 11(1); e03263-19
29. Lambertz J, Weiskirchen S, Landert S, Fructose: A dietary sugar in crosstalk with microbiota contributing to the development and progression of non-alcoholic liver disease: Front Immunol, 2017; 8; 1159
30. Volynets V, Louis S, Pretz D, Intestinal barrier function and the gut microbiome are differentially affected in mice fed a western-style diet or drinking water supplemented with fructose: J Nutr, 2017; 147(5); 770-80
31. Trigueros L, Peña S, Ugidos AV, Food ingredients as anti-obesity agents: A review: Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, 2013; 53(9); 929-42
32. Cui Y, Wang Q, Chang R, Intestinal barrier function-non-alcoholic fatty liver disease interactions and possible role of gut microbiota: J Agric Food Chem, 2019; 67(10); 2754-62
33. Feng D, Zou J, Su D, Curcumin prevents high-fat diet-induced hepatic steatosis in ApoE mice by improving intestinal barrier function and reducing endotoxin and liver TLR4/NF-κB inflammation: Nutr Metab (Lond), 2019; 16; 79
34. Del Chierico F, Nobili V, Vernocchi P, Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach: Hepatology (Baltimore, Md), 2017; 65(2); 451-64
35. Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2004; 101(44); 15718-23
36. Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest: Nature, 2006; 444(7122); 1027-31
37. Everard A, Belzer C, Geurts L, Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity: Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013; 110(22); 9066-71
38. Mu J, Tan F, Zhou X, Zhao X, Lactobacillus fermentum CQPC06 in naturally fermented pickles prevents non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by stabilizing the gut-liver axis in mice: Food Funct, 2020; 11(10); 8707-23
39. Zhang Y, Chen L, Hu M, Dietary type 2 resistant starch improves systemic inflammation and intestinal permeability by modulating microbiota and metabolites in aged mice on high-fat diet: Aging, 2020; 12(10); 9173-87
40. Song JJ, Tian WJ, Kwok L-Y, Effects of microencapsulated Lactobacillus plantarum LIP-1 on the gut microbiota of hyperlipidaemic rats: Br J Nutr, 2017; 118(7); 481-92
41. Zhuang P, Zhang Y, Shou Q, Eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids differentially alter gut microbiome and reverse high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance: Mol Nutr Food Res, 2020; 64(10); e1900946
Figures
 Figure 1. LCBE prevents abnormal weight, liver weight, and liver index levels, and improves glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). (A) Body weight; (B) liver index; and (C) blood glucose concentration in the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT); (D) levels of serum insulin; and (E) determination of HOMA-IR. The data are expressed as means±SD. # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs Chow, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 1. LCBE prevents abnormal weight, liver weight, and liver index levels, and improves glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). (A) Body weight; (B) liver index; and (C) blood glucose concentration in the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT); (D) levels of serum insulin; and (E) determination of HOMA-IR. The data are expressed as means±SD. # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs Chow, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs HFD. Figure 2. Effect of LCBE on serum lipid metabolism, ALT, and AST levels in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Serum triglyceride; (B) serum total cholesterol; (C) serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; (D) serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; (E) activity of serum ALT; (F) activity of serum AST; (G) histopathology images of liver tissues ((I) H&E, 200× magnification; Oil Red O, 200× magnification); and (H) protein expression levels of PPAR-α and CPT-1 in the liver. GAPDH was used in the loading chow. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 2. Effect of LCBE on serum lipid metabolism, ALT, and AST levels in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Serum triglyceride; (B) serum total cholesterol; (C) serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; (D) serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; (E) activity of serum ALT; (F) activity of serum AST; (G) histopathology images of liver tissues ((I) H&E, 200× magnification; Oil Red O, 200× magnification); and (H) protein expression levels of PPAR-α and CPT-1 in the liver. GAPDH was used in the loading chow. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. Figure 3. LCBE mitigates systemic inflammation in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). The levels of (A, D) interleukin 1β (IL-1β), (B, E) interleukin 6 (IL-6), and (C, F) tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in the serum and liver. (G–H) Protein expression levels of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in the liver. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 3. LCBE mitigates systemic inflammation in mice fed a high-fat diet (HFD). The levels of (A, D) interleukin 1β (IL-1β), (B, E) interleukin 6 (IL-6), and (C, F) tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) in the serum and liver. (G–H) Protein expression levels of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in the liver. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. Figure 4. LCBE consolidates the intestinal barrier in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Histopathology images of intestine tissues (H&E, 200× magnification). (B) LPS levels in the serum. (C, D) Protein expression levels of occludin and Claudin1 in the intestine. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 4. LCBE consolidates the intestinal barrier in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Histopathology images of intestine tissues (H&E, 200× magnification). (B) LPS levels in the serum. (C, D) Protein expression levels of occludin and Claudin1 in the intestine. The data are expressed as means±SD. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. Figure 5. LCBE modulates the gut microbiota community in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Shannon curve of each sample. (B) Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of microbial communities based on the unweighted Unifrac cluster for each sample at the phylum level. (C) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of microbial communities based on the unweighted Unifrac cluster for each sample at the phylum level. (D) Relative abundance analysis of microbiota at the phylum level between groups. (E–J) Ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes and relative abundance of bacteria among groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 5. LCBE modulates the gut microbiota community in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Shannon curve of each sample. (B) Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of microbial communities based on the unweighted Unifrac cluster for each sample at the phylum level. (C) Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) of microbial communities based on the unweighted Unifrac cluster for each sample at the phylum level. (D) Relative abundance analysis of microbiota at the phylum level between groups. (E–J) Ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes and relative abundance of bacteria among groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. Figure 6. LCBE amends the gut microbiota at the genus level in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Taxonomic cladogram depicting enriched taxa that are differentially abundant in all groups with a LDA score >3.0. (B–O) Relative abundance of different bacteria in all groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD.
Figure 6. LCBE amends the gut microbiota at the genus level in mice fed a high-fat diet. (A) Taxonomic cladogram depicting enriched taxa that are differentially abundant in all groups with a LDA score >3.0. (B–O) Relative abundance of different bacteria in all groups. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 vs Chow, # P<0.05, ## P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs HFD. In Press
12 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Comparing Neuromuscular Blockade Measurement Between Upper Arm (TOF Cuff®) and Eyelid (TOF Scan®) Using Miv...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943630
11 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Enhancement of Frozen-Thawed Human Sperm Quality with Zinc as a Cryoprotective AdditiveMed Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.942946
12 Mar 2024 : Database Analysis
Risk Factors of Age-Related Macular Degeneration in a Population-Based Study: Results from SHIP-TREND-1 (St...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943140
12 Mar 2024 : Clinical Research
Preoperative Blood Transfusion Requirements for Hemorrhoidal Severe Anemia: A Retrospective Study of 128 Pa...Med Sci Monit In Press; DOI: 10.12659/MSM.943126
Most Viewed Current Articles
17 Jan 2024 : Review article
Vaccination Guidelines for Pregnant Women: Addressing COVID-19 and the Omicron VariantDOI :10.12659/MSM.942799
Med Sci Monit 2024; 30:e942799
14 Dec 2022 : Clinical Research
Prevalence and Variability of Allergen-Specific Immunoglobulin E in Patients with Elevated Tryptase LevelsDOI :10.12659/MSM.937990
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e937990
16 May 2023 : Clinical Research
Electrophysiological Testing for an Auditory Processing Disorder and Reading Performance in 54 School Stude...DOI :10.12659/MSM.940387
Med Sci Monit 2023; 29:e940387
01 Jan 2022 : Editorial
Editorial: Current Status of Oral Antiviral Drug Treatments for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Non-Hospitalized Pa...DOI :10.12659/MSM.935952
Med Sci Monit 2022; 28:e935952